Comparison of Endoscopic Tympanoplasty to Microscopic Tympanoplasty
- PMID: 27334511
- PMCID: PMC5327595
- DOI: 10.21053/ceo.2016.00080
Comparison of Endoscopic Tympanoplasty to Microscopic Tympanoplasty
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to compare the outcome of endoscopic and microscopic tympanoplasty.
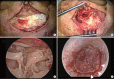
Methods: This was a retrospective comparative study of 73 patients (35 males and 38 females) who underwent type I tympanoplasty at Samsung Medical Center from April to December 2014. The subjects were classified into two groups; endoscopic tympanoplasty (ET, n=25), microscopic tympanoplasty (MT, n=48). Demographic data, perforation size of tympanic membrane at preoperative state, pure tone audiometric results preoperatively and 3 months postoperatively, operation time, sequential postoperative pain scale (NRS-11), and graft success rate were evaluated.
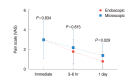
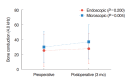
Results: The perforation size of the tympanic membrane in ET and MT group was 25.3%±11.7% and 20.1%±11.9%, respectively (P=0.074). Mean operation time of MT (88.9±28.5 minutes) was longer than that of the ET (68.2±22.1 minutes) with a statistical significance (P=0.002). External auditory canal (EAC) width was shorter in the ET group than in the MT group (P=0.011). However, EAC widening was not necessary in the ET group and was performed in 33.3% of patients in the MT group. Graft success rate in the ET and MT group were 100% and 95.8%, respectively; the values were not significantly different (P=0.304). Pre- and postoperative audiometric results including bone and air conduction thresholds and air-bone gap were not significantly different between the groups. In all groups, the postoperative air-bone gap was significantly improved compared to the preoperative air-bone gap. Immediate postoperative pain was similar between the groups. However, pain of 1 day after surgery was significantly less in the ET group.
Conclusion: With endoscopic system, minimal invasive tympanoplasty can be possible with similar graft success rate and less pain.
Keywords: Endoscopy; Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedures; Pain; Tympanoplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Zollner F. The principles of plastic surgery of the sound-conducting apparatus. J Laryngol Otol. 1955 Oct;69(10):637–52. - PubMed
-
- Dornhoffer JL. Hearing results with cartilage tympanoplasty. Laryngoscope. 1997 Aug;107(8):1094–9. - PubMed
-
- Thomassin JM, Duchon-Doris JM, Emram B, Rud C, Conciatori J, Vilcoq P. Endoscopic ear surgery: initial evaluation. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 1990;107(8):564–70. - PubMed
-
- Marchioni D, Alicandri-Ciufelli M, Piccinini A, Genovese E, Presutti L. Inferior retrotympanum revisited: an endoscopic anatomic study. Laryngoscope. 2010 Sep;120(9):1880–6. - PubMed
-
- Ayache S, Tramier B, Strunski V. Otoendoscopy in cholesteatoma surgery of the middle ear: what benefits can be expected? Otol Neurotol. 2008 Dec;29(8):1085–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

