Differential responses of Trans-Resveratrol on proliferation of neural progenitor cells and aged rat hippocampal neurogenesis
- PMID: 27334554
- PMCID: PMC4917886
- DOI: 10.1038/srep28142
Differential responses of Trans-Resveratrol on proliferation of neural progenitor cells and aged rat hippocampal neurogenesis
Abstract
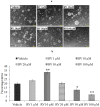
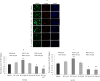
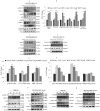
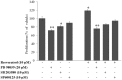
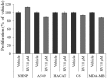
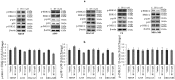
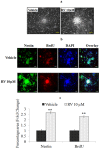
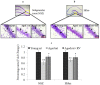
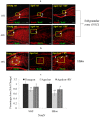
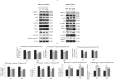
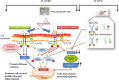
The plethora of literature has supported the potential benefits of Resveratrol (RV) as a life-extending as well as an anticancer compound. However, these two functional discrepancies resulted at different concentration ranges. Likewise, the role of Resveratrol on adult neurogenesis still remains controversial and less understood despite its well documented health benefits. To gather insight into the biological effects of RV on neurogenesis, we evaluated the possible effects of the compound on the proliferation and survival of neural progenitor cells (NPCs) in culture, and in the hippocampus of aged rats. Resveratrol exerted biphasic effects on NPCs; low concentrations (10 μM) stimulated cell proliferation mediated by increased phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) and p38 kinases, whereas high concentrations (>20 μM) exhibited inhibitory effects. Administration of Resveratrol (20 mg/kg body weight) to adult rats significantly increased the number of newly generated cells in the hippocampus, with upregulation of p-CREB and SIRT1 proteins implicated in neuronal survival and lifespan extension respectively. We have successfully demonstrated that Resveratrol exhibits dose dependent discrepancies and at a lower concentration can have a positive impact on the proliferation, survival of NPCs and aged rat hippocampal neurogenesis implicating its potential as a candidate for restorative therapies against age related disorders.
Figures

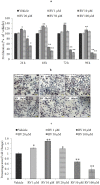
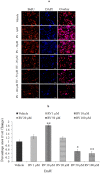
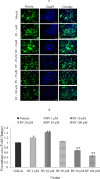
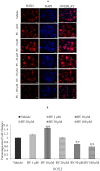
References
-
- Taupin P. & Gage F. H. Adult neurogenesis and neural stem cells of the central nervous system in mammals. Journal of neuroscience research 69, 745–749 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Lee J., Duan W., Long J. M., Ingram D. K. & Mattson M. P. Dietary restriction increases the number of newly generated neural cells, and induces BDNF expression, in the dentate gyrus of rats. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience 15, 99–108 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Lee J., Seroogy K. B. & Mattson M. P. Dietary restriction enhances neurotrophin expression and neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult mice. Journal of neurochemistry 80, 539–547 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Van Praag H., Kempermann G. & Gage F. H. Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nature neuroscience 2, 266–270 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

