Management of granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease in a patient with common variable immune deficiency
- PMID: 27335365
- PMCID: PMC4932434
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2016-215624
Management of granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease in a patient with common variable immune deficiency
Abstract
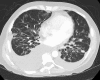
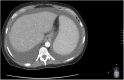
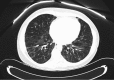
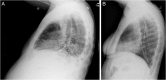
A 61-year-old woman presented with longstanding cough and progressive dyspnoea. She underwent an extensive evaluation and was diagnosed with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) with granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD). She was initially treated with subcutaneous immunoglobulin therapy, having declined intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy. She also declined treatment with oral glucocorticoids. Over several months, she became increasingly symptomatic and developed increased pulmonary infiltrates, pleural effusions, mediastinal adenopathy, splenomegaly, pancytopenia and ascites. An interdisciplinary team composed of an immunologist, pulmonologist and haematologist deliberated over a therapeutic management approach. The patient received a recently reported immunotherapy regimen with azathioprine and rituximab. The therapy led to rapid improvement of her constitutional and respiratory symptoms, with clinical and radiographic improvement in her interstitial lung disease, lymphadenopathy, pleural effusions and ascites. This case report reviews the literature surrounding the diagnosis and management of GLILD.
2016 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
