Ganoderma Lucidum polysaccharides protect against MPP(+) and rotenone-induced apoptosis in primary dopaminergic cell cultures through inhibiting oxidative stress
- PMID: 27335703
- PMCID: PMC4913221
Ganoderma Lucidum polysaccharides protect against MPP(+) and rotenone-induced apoptosis in primary dopaminergic cell cultures through inhibiting oxidative stress
Abstract
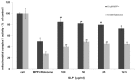
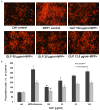
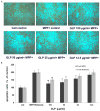
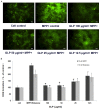
Oxidative stress plays a pivotal role in the progressive neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease (PD) which is responsible for disabling motor abnormalities in more than 6.5 million people worldwide. Polysaccharides are the main active constituents from Ganoderma lucidum which is characterized with anti-oxidant, antitumor and immunostimulant properties. In the present study, primary dopaminergic cell cultures prepared from embryonic mouse mesencephala were used to investigate the neuroprotective effects and the potential mechanisms of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides (GLP) on the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons induced by the neurotoxins methyl-4-phenylpyridine (MPP(+)) and rotenone. Results revealed that GLP can protect dopamine neurons against MPP(+) and rotenone at the concentrations of 100, 50 and 25 μg/ml in primary mesencephalic cultures in a dose-dependent manner. Interestingly, either with or without neurotoxin treatment, GLP treatment elevated the survival of THir neurons, and increased the length of neurites of dopaminergic neurons. The Trolox equivalent anti-oxidant capacity (TEAC) of GLP was determined to be 199.53 μmol Trolox/g extract, and the decrease of mitochondrial complex I activity induced by MPP(+) and rotenone was elevated by GLP treatment (100, 50, 25 and 12.5 μg/ml) in a dose dependent manner. Furthermore, GLP dramatically decreased the relative number of apoptotic cells and increased the declining mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) induced by MPP(+) and rotenone in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, GLP treatment reduced the ROS formation induced by MPP(+) and rotenone at the concentrations of 100, 50 and 25 μg/ml in a dose-dependent manner. Our study indicates that GLP possesses neuroprotective properties against MPP(+) and rotenone neurotoxicity through suppressing oxidative stress in primary mesencephalic dopaminergic cell culture owning to its antioxidant activities.
Keywords: Ganoderma Lucidum polysaccharides; MPP+; Parkinson’s disease; oxidative stress; rotenone.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effect of rotigotine against complex I inhibitors, MPP⁺ and rotenone, in primary mesencephalic cell culture.Folia Neuropathol. 2014;52(2):179-86. doi: 10.5114/fn.2014.43789. Folia Neuropathol. 2014. PMID: 25118903
-
Thymoquinone protects dopaminergic neurons against MPP+ and rotenone.Phytother Res. 2009 May;23(5):696-700. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2708. Phytother Res. 2009. PMID: 19089849
-
Human dental pulp stem cells protect mouse dopaminergic neurons against MPP+ or rotenone.Brain Res. 2011 Jan 7;1367:94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.09.042. Epub 2010 Sep 18. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 20854799
-
Research progress of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide in prevention and treatment of Atherosclerosis.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 19;10(12):e33307. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33307. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39022015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the anti-cancer potential of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides (GLPs) and their versatile role in enhancing drug delivery systems: a multifaceted approach to combat cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Dec 16;23(1):324. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03146-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 38104078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple Metabolites Derived from Mushrooms and Their Beneficial Effect on Alzheimer's Diseases.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 15;15(12):2758. doi: 10.3390/nu15122758. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37375662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of natural products to inhibit abnormal aggregation of α-Synuclein in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 23;15:1468850. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1468850. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39508052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low Molecular Weight Sulfated Chitosan: Neuroprotective Effect on Rotenone-Induced In Vitro Parkinson's Disease.Neurotox Res. 2019 Apr;35(3):505-515. doi: 10.1007/s12640-018-9978-z. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Neurotox Res. 2019. PMID: 30426393
-
EriB targeted inhibition of microglia activity attenuates MPP+ induced DA neuron injury through the NF-κB signaling pathway.Mol Brain. 2018 Dec 18;11(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13041-018-0418-z. Mol Brain. 2018. PMID: 30563578 Free PMC article.
-
The Biological Activity of Ganoderma lucidum on Neurodegenerative Diseases: The Interplay between Different Active Compounds and the Pathological Hallmarks.Molecules. 2024 May 26;29(11):2516. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112516. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893392 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antony PM, Diederich NJ, Kruger R, Balling R. The hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease. FEBS J. 2013;280:5981–5993. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
