Serum Levels of Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-10 as Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Egyptian Patients
- PMID: 27335826
- PMCID: PMC4890868
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/412317
Serum Levels of Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-10 as Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Egyptian Patients
Abstract
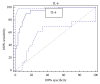
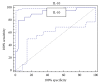
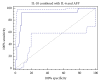
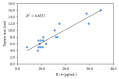
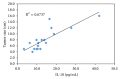
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) have been reported to be related to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) prognosis. This study aimed to investigate the clinical usefulness of serum levels of IL-6 and IL-10 as biomarkers for HCC among high-risk patients. Materials and Methods. 80 individuals were enrolled in this study; they were categorized into 4 groups: group 1 healthy individuals (NC) (n = 20), group 2 chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) patients (n = 20), group 3 cirrhotic patients (LC) (n = 20), and HCC group (n = 20). Using ELISA technique serum levels of IL-6, IL-10, and alpha fetoprotein (AFP) were evaluated in all groups. Results. The mean serum levels of IL-6 were significantly higher in HCC than in LC, HCV, and NC groups (13.99 ± 1.80, 7.49 ± 0.43, 5.78 ± 0.74, and 2.57 ± 0.31), respectively (P < 0.05); also the serum levels of IL-10 were significantly higher in HCC compared with LC, HCV, and NC groups (13.69 ± 1.89, 7.37 ± 0.53, 5.18 ± 0.6, and 3.31 ± 0.42) (P < 0.05). We also found that the tumor size is correlated strongly with IL-6 and IL-10 levels (r = 0.925, P < 0.001; r = 0.821, P < 0.001), respectively. Conclusion. The combination of those markers may help to identify a group of HCC patients with low AFP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Significance of hsa-miR-21-5p, hsa-miR-192-5p, hsa-miR-155-5p, hsa-miR-199a-5p Panel and Ratios in Hepatocellular Carcinoma on Top of Liver Cirrhosis in HCV-Infected Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 5;24(4):3157. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043157. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834570 Free PMC article.
-
[Usefulness of serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) as a marker for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in hepatitis C virus related cirrhosis: analysis of the factors influencing AFP elevation without HCC development].Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006 Nov;48(5):321-6. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17132920 Clinical Trial. Korean.
-
Impact of interleukin IL-6 rs-1474347 and IL-10 rs-1800896 genetic polymorphisms on the susceptibility of HCV-infected Egyptian patients to hepatocellular carcinoma.Immunol Res. 2020 Jun;68(3):118-125. doi: 10.1007/s12026-020-09126-8. Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 32504406
-
Role of interleukin-8 and oxidative stress in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Lab. 2013;59(9-10):969-76. doi: 10.7754/clin.lab.2012.120712. Clin Lab. 2013. PMID: 24273918
-
Serum biomarkers for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with HCV infection in egyptian patients.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(3):1281-7. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.3.1281. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 25735368
Cited by
-
The IL6-174G/C Polymorphism Associated with High Levels of IL-6 Contributes to HCV Infection, but Is Not Related to HBV Infection, in the Amazon Region of Brazil.Viruses. 2022 Feb 28;14(3):507. doi: 10.3390/v14030507. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35336914 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Alcohol Consumption Promotes Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis via Immune Disturbances.Sci Rep. 2017 May 31;7(1):2567. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02887-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28566719 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of serum interleukin-6 levels in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018 Sep;4(3):182-190. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2018.78122. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30324143 Free PMC article.
-
Origin and role of hepatic myofibroblasts in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2020 Mar 31;11(13):1186-1201. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27532. eCollection 2020 Mar 31. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 32284794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of serum interleukin-10 levels in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018 Mar;4(1):35-40. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2018.73484. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29594196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attalla S. M., El-Azab S. M., El-Bakary A. A., et al. Is aflatoxin B1 a common risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma? Mansoura Journal of Forensic Medicine and Clinical Toxicology. 2009;17(2):15–24.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
