Improved Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein Levels after Iron Reduction Therapy in HCV Patients
- PMID: 27335844
- PMCID: PMC4890901
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/875140
Improved Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein Levels after Iron Reduction Therapy in HCV Patients
Abstract
Background and Aims. To examine the changes in serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels after iron reduction by therapeutic phlebotomy in chronic hepatitis C patients. Methods. This retrospective study included 26 chronic hepatitis C patients. The patients were developed iron depletion by repeated therapeutic phlebotomies. Results. Iron reduction therapy significantly reduced the median level of serum AFP from 13 to 7 ng/mL, ALT from 96 to 50 IU/L, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) from 55 to 28 IU/L, and ferritin from 191 to 10 ng/mL (P < 0.001 for each). The rate of decline in the AFP level correlated positively only with that in GGT (r = 0.695, P = 0.001), although a spurious correlation was observed between the rates of decline for AFP and ALT. The AFP level normalized (<10 ng/mL) posttreatment in eight (50%) of 16 patients who had elevated pretreatment AFP levels. Normalized post-treatment ALT and GGT levels were seen in 12% (3 of 26) and 39% (7 of 18) of the patients, respectively. Multivariate analysis identified a post-treatment GGT level of <30 IU/L as an independent factor associated with post-treatment AFP normalization (odds ratio, 21; 95% confidence interval, 1.5-293; P = 0.024). Conclusions. Iron reduction by therapeutic phlebotomy can reduce serum AFP and GGT levels in chronic hepatitis C patients.
Figures
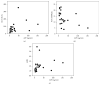
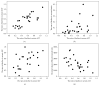
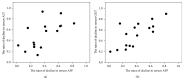
Similar articles
-
Elevated serum α-fetoprotein levels in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 4: not the end of the story.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Mar;28(3):313-22. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000534. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26618566
-
Predictors of alpha-fetoprotein elevation in patients with chronic hepatitis C, but not hepatocellular carcinoma, and its normalization after pegylated interferon alfa 2a-ribavirin combination therapy.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 May;22(5):669-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.04898.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. PMID: 17444854
-
Evaluation of Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein Level in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients.Clin Lab. 2019 Jan 1;65(1). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2018.180607. Clin Lab. 2019. PMID: 30775893
-
Change in γ-glutamyl transpeptidase activity as a useful tool in identifying a group of patients with elevated risk of hepatocellular carcinoma development after DAA treatment of chronic hepatitis C.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2021 Mar;7(1):93-100. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2021.104466. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34027121 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of serum ALT normalization after phlebotomy in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection.J Gastroenterol. 2005 Sep;40(9):901-6. doi: 10.1007/s00535-005-1636-6. J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16211347
Cited by
-
Ferritin level prospectively predicts hepatocarcinogenesis in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection.Oncol Lett. 2018 Sep;16(3):3499-3508. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9099. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30127954 Free PMC article.
-
Update on the applications and limitations of alpha-fetoprotein for hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Jan 14;28(2):216-229. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i2.216. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35110946 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis C. Global Alert and Response, Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2002, http://www.who.int/csr/disease/hepatitis/whocdscsrlyo2003/en/index.html.
-
- Johnson P. J. The role of serum alpha-fetoprotein estimation in the diagnosis and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clinics in Liver Disease. 2001;5(1):145–159. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
