Opioid Mechanism Involvement in the Synergism Produced by the Combination of Diclofenac and Caffeine in the Formalin Model
- PMID: 27335871
- PMCID: PMC4893401
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/196429
Opioid Mechanism Involvement in the Synergism Produced by the Combination of Diclofenac and Caffeine in the Formalin Model
Abstract
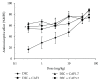
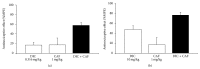
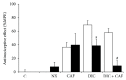
Analgesics can be administered in combination with caffeine for improved analgesic effectiveness in a process known as synergism. The mechanisms by which these combinations produce synergism are not yet fully understood. The aim of this study was to analyze whether the administration of diclofenac combined with caffeine produced antinociceptive synergism and whether opioid mechanisms played a role in this event. The formalin model was used to evaluate the antinociception produced by the oral administration of diclofenac, caffeine, or their combination. Opioid involvement was analyzed through intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of naloxone followed by the oral administration of the study drugs. Diclofenac presented a dose-dependent effect, with a mean effective dose (ED50) of 6.7 mg/kg. Caffeine presented an analgesic effect with a 17-36% range. The combination of subeffective doses of each of the two drugs presented the greatest synergism with an effect of 57.7 ± 5.6%. The maximal antinociceptive effect was obtained with the combination of 10.0 mg/kg diclofenac and 1.0 mg/kg of caffeine, with an effect of 76.7 ± 5.6%. The i.c.v. administration of naloxone inhibited the effect of diclofenac, both separately and combined. In conclusion, caffeine produces antinociceptive synergism when administered in combination with diclofenac, and this synergism is partially mediated by opioid mechanisms at the central level.
Figures

References
-
- Burke A., Smyth E., FitzGerald G. A. Analgesic-antypiretic agents; pharmacotherapy of gout. In: Brunton L. L., Lazo J. S., Parker K. L., editors. Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 11th. New York, NY, USA: McGraw Hill; 2006. pp. 697–698.
-
- Ku E. C., Lee W., Kothari H. V., Scholer D. W. Effect of diclofenac sodium on the arachidonic acid cascade. American Journal of Medicine. 1986;80(4):18–23. - PubMed
-
- Sacerdote P., Monza G., Mantegazza P., Paneri A. E. Diclofenac and pirprofen modify pituitary and hypothalamic beta-endorphin concentrations. Pharmacological Research Communications. 1985;17(8):679–684. - PubMed
-
- Bjorkman R. L., Hedner T., Hallman K. M., Henning M., Hedner J. Localization of the central antinociceptive effects of diclofenac in the rat. Brain Research. 1992;590(1-2):66–73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
