Preparation of Single Cell Suspensions from Mouse Aorta
- PMID: 27335895
- PMCID: PMC4913879
- DOI: 10.21769/bioprotoc.1832
Preparation of Single Cell Suspensions from Mouse Aorta
Abstract
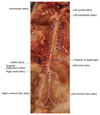
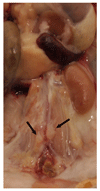
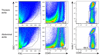
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the arterial wall characterized by lipid deposition, plaque formation, and immune cell infiltration. Innate and adaptive immune cells infiltrate the artery during development of the disease. Moreover, advanced disease leads to formation of artery tertiary lymphoid organs in the adventitia (Grabner et al., 2009; Hu et al., 2015). Various and diverse types of immune cells have been identified in the aorta adventitia vs atherosclerotic plaques (Elewa et al., 2016; Galkina et al., 2006; Lotzer et al., 2010; Mohanta et al., 2016; Mohanta et al., 2014; Moos et al., 2005; Srikakulapu et al., 2016; Zhao et al., 2004). There are conflicting reports on the number and subtypes of immune cells in the aorta depending on the age of the animals, the protocol that is used to obtain single cell suspensions, and the dietary conditions of the mice (Campbell et al., 2012; Clement et al., 2015; Galkina et al., 2006; Kyaw et al., 2012). The number of immune cells in the aorta differs as much as tenfold using different protocols (Butcher et al., 2012; Galkina et al., 2006; Gjurich et al., 2015; Grabner et al., 2009; Hu et al., 2015). These discrepant results call for a protocol that robustly documents bona fide aorta cells rather than those in the surrounding tissues or blood. Critical methodological hurdles include the removal of adjacent adipose tissue and small paraaortic lymph nodes lining the entire aortic tree that are not visible by the naked eye. A dissection microscope is therefore recommended. Moreover protocols of aorta preparations should ascertain that lymphocyte aggregates referred to as fat associated lymphoid clusters (FALCs) (Benezech et al., 2015; Elewa et al., 2015) that are often present at the border between the adipose tissue and the adventitia are removed before enzyme digestion. We propose - besides other approaches (Hu et al., 2015; Mohanta et al., 2014) - a combination of immunohistochemical staining and fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS) analyses from single cell suspensions to quantify the cells of interest. This protocol describes isolation of single cells from mouse aorta for FACS and other analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Clement M, Guedj K, Andreata F, Morvan M, Bey L, Khallou-Laschet J, Gaston AT, Delbosc S, Alsac JM, Bruneval P, Deschildre C, et al. Control of the T follicular helper-germinal center B-cell axis by CD8(+) regulatory T cells limits atherosclerosis and tertiary lymphoid organ development. Circulation. 2015;131(6):560–570. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

