Infantile Feeding Difficulties: It Is Not Always Reflux
- PMID: 27335912
- PMCID: PMC4804670
- DOI: 10.1177/2333794X14553624
Infantile Feeding Difficulties: It Is Not Always Reflux
Abstract
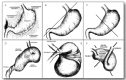
Background. Gastric volvulus refers to a torsion of all or part of the stomach that may cause an obstruction of the foregut. The clinical symptoms of gastric volvulus range from asymptomatic to life-threatening and thus must be rapidly diagnosed. However, the presenting symptoms of gastric volvulus vary widely, which may cause diagnosis to be delayed or missed. Objective. Describe varying presentations of gastric volvulus (including a case report of a rare presentation), pathophysiology of the entity, and how to diagnose/treat the phenomenon. Design/Method. Article review and case presentation. Results. Our patient was taken to the operating room for a gastropexy and G-tube placement. During surgery, the stomach was redundant and large, but not currently torsed, consistent with intermittent organoaxial volvulus. There are several approaches to classifying gastric volvulus as well as different theories on how to treat the volvulus based on type and degree of rotation that this article aims to detail more thoroughly. Conclusion. There are a growing number of case reports describing gastric volvulus, which had historically been viewed as a rare finding. The presenting symptoms of gastric volvulus commonly mimic other, more benign newborn diagnoses, and thus can be difficult to diagnose. We present our patient as well as an article review of other cases to highlight the diverse presentations of gastric volvulus so this potentially devastating disease can be diagnosed quickly with prompt treatment initiation.
Keywords: critical care; emergency medicine; gastroenterology; general pediatrics; neonatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acute Organoaxial gastric volvulus: A massive problem with a twist-case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2017;41:366-369. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2017.11.016. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 29156231 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic gastric volvulus with diaphragmatic eventration: Case presentation.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024 Jan;114:109095. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.109095. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38035865 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Gastric Volvulus Causing Splenic Avulsion and Hemoperitoneum.Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2018 Apr 1;2018:2961063. doi: 10.1155/2018/2961063. eCollection 2018. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2018. PMID: 29805820 Free PMC article.
-
[Gastric volvulus: diagnosis and management].Presse Med. 2008 Mar;37(3 Pt 2):e67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2007.03.043. Epub 2007 Jun 22. Presse Med. 2008. PMID: 17587536 Review. French.
-
[Acute gastric volvulus: late complication of Nissen fundoplication. Report of two cases and review of the literature].Cir Cir. 2014 Sep-Oct;82(5):541-50. Cir Cir. 2014. PMID: 25259434 Review. Spanish.
References
-
- Mayo A, Erez I, Lazar L, Rathaus V, Konen O, Freud E. Volvulus of the stomach in childhood: the spectrum of the disease. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2001;17:344-348. - PubMed
-
- Cribbs RK, Gow KW, Wulkan ML. Gastric volvulus in infants and children. Pediatrics. 2008;122:e752-e762. - PubMed
-
- Oh SK, Han BK, Levin TL, Murphy R, Blitman NM, Ramos C. Gastric volvulus in children: the twists and turns of an unusual entity. Pediatr Radiol. 2008;38:297-304. - PubMed
-
- Chattopadhyay A. Neonatal gastric volvulus: another cause of “mucousy baby” with gasless abdomen. Indian J Pediatr. 2010;77:691-692. - PubMed
-
- Anagnostara A, Koumanidou C, Vakaki M, Manoli E, Kakavakis K. Chronic gastric volvulus and hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in an infant. J Clin Ultrasound. 2003;31:383-386. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

