The Difficult Task of Evaluating MDG-4: Monitoring Trends in Child Survival in Africa
- PMID: 27335957
- PMCID: PMC4784596
- DOI: 10.1177/2333794X15584622
The Difficult Task of Evaluating MDG-4: Monitoring Trends in Child Survival in Africa
Abstract
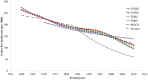
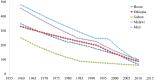
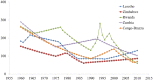
Background. The fourth Millennium Development Goal (MDG-4) proposed to reduce under-5 mortality rates (U5MR) by two thirds within 25 years. The article discusses changes in U5MR for 35 sub-Saharan African countries, for which DHS surveys are available. Methods. Analysis of DHS data, reconstruction of time series of U5MR, and comparison with other series. Findings. Few countries were able to achieve MDG-4 from 1985 to 2010, and the few who did seem to have achieved the goal apparently either because of abnormally high baseline or a surprisingly low endpoint. If all countries experienced significant mortality decline, only a minority had a steady decline, and many had periods of rising and falling mortality, for a variety of reasons. Interpretation. Discussion focuses on data quality, on methods for estimating levels and trends in under-5 mortality, and on the circumstances explaining rises and falls in mortality. MDG-4 appeared overambitious for Africa, given high mortality levels, political instability, economic crises, and above all emerging diseases, in particular HIV/AIDS. The last 10 years from 2000 to 2010 appeared as the most favorable period since 1960 in African countries, with the exception of countries with widespread HIV/AIDS.
Keywords: HIV/AIDS; Millennium Development Goals (MDG); emerging diseases; health transition; malaria; sub-Saharan Africa; under-5 mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health transitions in sub-Saharan Africa: overview of mortality trends in children under 5 years old (1950-2000).Bull World Health Organ. 2006 Jun;84(6):470-8. doi: 10.2471/blt.05.029231. Epub 2006 Jun 21. Bull World Health Organ. 2006. PMID: 16799731 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the HIV epidemic on mortality in sub-Saharan Africa: evidence from national surveys and censuses.AIDS. 1998;12 Suppl 1:S15-27. AIDS. 1998. PMID: 9677186 Review.
-
The effect of an integrated multisector model for achieving the Millennium Development Goals and improving child survival in rural sub-Saharan Africa: a non-randomised controlled assessment.Lancet. 2012 Jun 9;379(9832):2179-88. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60207-4. Epub 2012 May 8. Lancet. 2012. PMID: 22572602 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of illicit financial flows on time to reach the fourth Millennium Development Goal in Sub-Saharan Africa: a quantitative analysis.J R Soc Med. 2014 Apr;107(4):148-56. doi: 10.1177/0141076813514575. Epub 2013 Dec 13. J R Soc Med. 2014. PMID: 24334911 Free PMC article.
-
Projecting the impact of AIDS on mortality.AIDS. 1998;12 Suppl 1:S29-39. AIDS. 1998. PMID: 9677187 Review.
References
-
- United Nations General Assembly. United Nations Millennium Declaration. A/RES/55. New York, NY, United Nations; http://www.un.org/millennium/declaration/ares552e.htm. Published 2000. Accessed February 17, 2006.
-
- Easterly W. How the Millennium Development Goals are unfair to Africa. World Dev. 2009;37(1):26-35.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

