Aerobic exercise and yoga improve neurocognitive function in women with early psychosis
- PMID: 27336050
- PMCID: PMC4849465
- DOI: 10.1038/npjschz.2015.47
Aerobic exercise and yoga improve neurocognitive function in women with early psychosis
Abstract
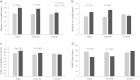
Impairments of attention and memory are evident in early psychosis, and are associated with functional disability. In a group of stable, medicated women patients, we aimed to determine whether participating in aerobic exercise or yoga improved cognitive impairments and clinical symptoms. A total of 140 female patients were recruited, and 124 received the allocated intervention in a randomized controlled study of 12 weeks of yoga or aerobic exercise compared with a waitlist group. The primary outcomes were cognitive functions including memory and attention. Secondary outcome measures were the severity of psychotic and depressive symptoms, and hippocampal volume. Data from 124 patients were included in the final analysis based on the intention-to-treat principle. Both yoga and aerobic exercise groups demonstrated significant improvements in working memory (P<0.01) with moderate to large effect sizes compared with the waitlist control group. The yoga group showed additional benefits in verbal acquisition (P<0.01) and attention (P=0.01). Both types of exercise improved overall and depressive symptoms (all P⩽0.01) after 12 weeks. Small increases in hippocampal volume were observed in the aerobic exercise group compared with waitlist (P=0.01). Both types of exercise improved working memory in early psychosis patients, with yoga having a larger effect on verbal acquisition and attention than aerobic exercise. The application of yoga and aerobic exercise as adjunctive treatments for early psychosis merits serious consideration. This study was supported by the Small Research Funding of the University of Hong Kong (201007176229), and RGC funding (C00240/762412) by the Authority of Research, Hong Kong.
Conflict of interest statement
EYHC sat on a scientific advisory board for Otsuka, received educational grant support from Janssen-Cilag, and research funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen-Cilag, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Sanofi-Aventis, and Otsuka. WGH received consulting fees or participated in paid advisory boards for In Silico Biosciences, Lundbeck/Otsuka, Eli Lilly and Roche. EHML sat on a scientific advisory board for AstraZeneca and Eli Lilly. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rund, B. R. A review of longitudinal studies of cognitive function in schizophrenia patients. Schizophr. Bull. 24, 425 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Malla, A. , Norman, R. , Manchanda, R. & Townsend, L. Symptoms, cognition, treatment adherence and functional outcome in first-episode psychosis. Psychol. Med. 32, 1109–1119 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Bilder, R. M. et al. Neuropsychology of first-episode schizophrenia: initial characterization and clinical correlates. Am. J. Psychiatry 157, 549–559 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Keefe, R. S. et al. Effects of olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone on neurocognitive function in early psychosis: a randomized, double-blind 52-week comparison. Am. J. Psychiatry 164, 1061–1071 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Vancampfort, D. et al. Systematic review of the benefits of physical therapy within a multidisciplinary care approach for people with schizophrenia. Phys. Ther. 92, 11–23 (2012). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

