Cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes prevent cardiomyocytes apoptosis through exosomal miR-21 by targeting PDCD4
- PMID: 27336721
- PMCID: PMC5143405
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2016.181
Cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes prevent cardiomyocytes apoptosis through exosomal miR-21 by targeting PDCD4
Abstract
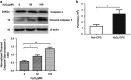
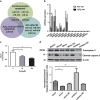
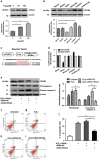
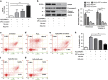
Cardiac progenitor cells derived from adult heart have emerged as one of the most promising stem cell types for cardiac protection and repair. Exosomes are known to mediate cell-cell communication by transporting cell-derived proteins and nucleic acids, including various microRNAs (miRNAs). Here we investigated the cardiac progenitor cell (CPC)-derived exosomal miRNAs on protecting myocardium under oxidative stress. Sca1(+)CPCs-derived exosomes were purified from conditional medium, and identified by nanoparticle trafficking analysis (NTA), transmission electron microscopy and western blotting using CD63, CD9 and Alix as markers. Exosomes production was measured by NTA, the result showed that oxidative stress-induced CPCs secrete more exosomes compared with normal condition. Although six apoptosis-related miRNAs could be detected in two different treatment-derived exosomes, only miR-21 was significantly upregulated in oxidative stress-induced exosomes compared with normal exosomes. The same oxidative stress could cause low miR-21 and high cleaved caspase-3 expression in H9C2 cardiac cells. But the cleaved caspase-3 was significantly decreased when miR-21 was overexpressed by transfecting miR-21 mimic. Furthermore, miR-21 mimic or inhibitor transfection and luciferase activity assay confirmed that programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) was a target gene of miR-21, and miR-21/PDCD4 axis has an important role in anti-apoptotic effect of H9C2 cell. Western blotting and Annexin V/PI results demonstrated that exosomes pre-treated H9C2 exhibited increased miR-21 whereas decreased PDCD4, and had more resistant potential to the apoptosis induced by the oxidative stress, compared with non-treated cells. These findings revealed that CPC-derived exosomal miR-21 had an inhibiting role in the apoptosis pathway through downregulating PDCD4. Restored miR-21/PDCD4 pathway using CPC-derived exosomes could protect myocardial cells against oxidative stress-related apoptosis. Therefore, exosomes could be used as a new therapeutic vehicle for ischemic cardiac disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate cardiomyocyte apoptosis in hypoxic conditions through microRNA144 by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Jan 23;11(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-1563-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 31973741 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-21 protects C-kit+ cardiac stem cells from oxidative injury through the PTEN/PI3K/Akt axis.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 14;13(2):e0191616. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191616. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29444190 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB mediated miR-21 regulation in cardiomyocytes apoptosis under oxidative stress.Free Radic Res. 2014 Mar;48(3):282-91. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2013.865839. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Free Radic Res. 2014. PMID: 24237305
-
Cardiac Progenitor-Cell Derived Exosomes as Cell-Free Therapeutic for Cardiac Repair.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;998:207-219. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-4397-0_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28936742 Review.
-
Cardioprotective microRNAs: Lessons from stem cell-derived exosomal microRNAs to treat cardiovascular disease.Atherosclerosis. 2019 Jun;285:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.03.016. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Atherosclerosis. 2019. PMID: 30939341 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Inactivation of the Proteasome Augments Alveolar Macrophage Secretion of Vesicular SOCS3.Cells. 2020 Jun 30;9(7):1589. doi: 10.3390/cells9071589. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32630102 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of sphingolipids and extracellular vesicles in development and therapeutics of cardiovascular diseases.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024 Jul 23;53:101469. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101469. eCollection 2024 Aug. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024. PMID: 39139609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocyte-derived exosomal MiR-194 activates PMVECs and promotes angiogenesis in hepatopulmonary syndrome.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Nov 7;10(11):853. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2087-y. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31700002 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-Derived Exosomal MicroRNA-25-3p Inhibits Coronary Vascular Endothelial Cell Inflammation Through Adam10 via the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in ApoE-/- Mice.Front Immunol. 2019 Oct 2;10:2205. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02205. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. Retraction in: Front Immunol. 2024 May 14;15:1429708. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1429708. PMID: 31632389 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Role of cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosome-mediated microRNA-210 in cardiovascular disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Nov;23(11):7124-7131. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14562. Epub 2019 Sep 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31557390 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lefer DJ, Granger DN. Oxidative stress and cardiac disease. Am J Med 2000; 109: 315–323. - PubMed
-
- Cantor EJ, Mancini EV, Seth R, Yao XH, Netticadan T. Oxidative stress and heart disease: cardiac dysfunction, nutrition, and gene therapy. Curr Hypertens Rep 2003; 5: 215–220. - PubMed
-
- Barile L, Lionetti V, Cervio E, Matteucci M, Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM et al. Extracellular vesicles from human cardiac progenitor cells inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res 2014; 103: 530–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

