Comparative Characterization of Shiga Toxin Type 2 and Subtilase Cytotoxin Effects on Human Renal Epithelial and Endothelial Cells Grown in Monolayer and Bilayer Conditions
- PMID: 27336788
- PMCID: PMC4918929
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158180
Comparative Characterization of Shiga Toxin Type 2 and Subtilase Cytotoxin Effects on Human Renal Epithelial and Endothelial Cells Grown in Monolayer and Bilayer Conditions
Abstract
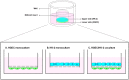
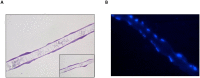
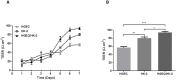
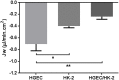
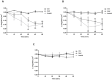
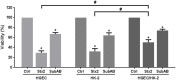
Postdiarrheal hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) affects children under 5 years old and is responsible for the development of acute and chronic renal failure, particularly in Argentina. This pathology is a complication of Shiga toxin (Stx)-producing Escherichia coli infection and renal damage is attributed to Stx types 1 and 2 (Stx1, Stx2) produced by Escherichia coli O157:H7 and many other STEC serotypes. It has been reported the production of Subtilase cytotoxin (SubAB) by non-O157 STEC isolated from cases of childhood diarrhea. Therefore, it is proposed that SubAB may contribute to HUS pathogenesis. The human kidney is the most affected organ because very Stx-sensitive cells express high amounts of biologically active receptor. In this study, we investigated the effects of Stx2 and SubAB on primary cultures of human glomerular endothelial cells (HGEC) and on a human tubular epithelial cell line (HK-2) in monoculture and coculture conditions. We have established the coculture as a human renal proximal tubule model to study water absorption and cytotoxicity in the presence of Stx2 and SubAB. We obtained and characterized cocultures of HGEC and HK-2. Under basal conditions, HGEC monolayers exhibited the lowest electrical resistance (TEER) and the highest water permeability, while the HGEC/HK-2 bilayers showed the highest TEER and the lowest water permeability. In addition, at times as short as 20-30 minutes, Stx2 and SubAB caused the inhibition of water absorption across HK-2 and HGEC monolayers and this effect was not related to a decrease in cell viability. However, toxins did not have inhibitory effects on water movement across HGEC/HK-2 bilayers. After 72 h, Stx2 inhibited the cell viability of HGEC and HK-2 monolayers, but these effects were attenuated in HGEC/HK-2 bilayers. On the other hand, SubAB cytotoxicity shows a tendency to be attenuated by the bilayers. Our data provide evidence about the different effects of these toxins on the bilayers respect to the monolayers. This in vitro model of communication between human renal microvascular endothelial cells and human proximal tubular epithelial cells is a representative model of the human proximal tubule to study the effects of Stx2 and SubAB related to the development of HUS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ouabain Protects Human Renal Cells against the Cytotoxic Effects of Shiga Toxin Type 2 and Subtilase Cytotoxin.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Jul 18;9(7):226. doi: 10.3390/toxins9070226. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28718802 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between Human Microvascular Endothelial Cells and Tubular Epithelial Cells Modulates Pro-Inflammatory Responses Induced by Shiga Toxin Type 2 and Subtilase Cytotoxin.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Nov 7;11(11):648. doi: 10.3390/toxins11110648. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31703347 Free PMC article.
-
Action of shiga toxin type-2 and subtilase cytotoxin on human microvascular endothelial cells.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 30;8(7):e70431. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070431. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936204 Free PMC article.
-
Host response to the subtilase cytotoxin produced by locus of enterocyte effacement-negative Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli.Microbiol Immunol. 2020 Oct;64(10):657-665. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12841. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Microbiol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32902863 Review.
-
A dietary non-human sialic acid may facilitate hemolytic-uremic syndrome.Kidney Int. 2009 Jul;76(2):140-4. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.131. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Kidney Int. 2009. PMID: 19387473 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toxins of Locus of Enterocyte Effacement-Negative Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Jun 14;10(6):241. doi: 10.3390/toxins10060241. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29903982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Action of Shiga Toxin Type 2 and Subtilase Cytotoxin in the Pathogenesis of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jul 29;13(8):536. doi: 10.3390/toxins13080536. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34437406 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of inhibition of Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli SubAB cytotoxicity by steroids and diacylglycerol analogues.Cell Death Discov. 2018 Feb 14;4:22. doi: 10.1038/s41420-017-0007-4. eCollection 2018 Dec. Cell Death Discov. 2018. PMID: 29531819 Free PMC article.
-
Shiga Toxin (Stx)-Binding Glycosphingolipids of Primary Human Renal Cortical Epithelial Cells (pHRCEpiCs) and Stx-Mediated Cytotoxicity.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Feb 12;13(2):139. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020139. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33673393 Free PMC article.
-
Ouabain Protects Human Renal Cells against the Cytotoxic Effects of Shiga Toxin Type 2 and Subtilase Cytotoxin.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Jul 18;9(7):226. doi: 10.3390/toxins9070226. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28718802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karmali MA, Petric M, Lim C, Fleming PC, Arbus GS, Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985;151(5):775–82. Epub 1985/05/01. . - PubMed
-
- Karpman D. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Current Paediatrics. 2002;12:569–74.
-
- Repetto HA. Epidemic hemolytic-uremic syndrome in children. Kidney Int. 1997;52(6):1708–19. Epub 1998/01/04. S0085-2538(15)60348-9 [pii]. . - PubMed
-
- Repetto HA. Microangiopatía trombótica y Sindrome Hemolítico Urémico. Nefrología Clínica 3ra edición 2009:286–97.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

