Mechanism-Based Inhibition of CYP3A4 by Podophyllotoxin: Aging of an Intermediate Is Important for in Vitro/in Vivo Correlations
- PMID: 27336918
- PMCID: PMC5059843
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.6b00436
Mechanism-Based Inhibition of CYP3A4 by Podophyllotoxin: Aging of an Intermediate Is Important for in Vitro/in Vivo Correlations
Abstract
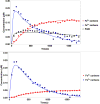
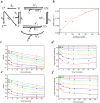
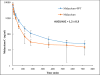
An in vitro observation of time-dependent inhibition (TDI) of metabolic enzymes often results in removing a potential drug from the drug pipeline. However, the accepted method for predicting TDIs of the important drug metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes often overestimates the drug interaction potential. Better models that take into account the complexities of the cytochrome P450 enzyme system will lead to better predictions. Herein we report the use of our previously described models for complex kinetics of podophyllotoxin. Spectral characterization of the kinetics indicates that an intermediate MI complex is formed, which slowly progresses to an essentially irreversible MI complex. The intermediate MI complex can release free enzyme during the time course of a typical 30 min TDI experiment. This slow rate of MI complex conversion results in an overprediction of the kinact value if this process is not included in the analysis of the activity versus time profile. In vitro kinetic experiments in rat liver microsomes predicted a lack of drug interaction between podophyllotoxin and midazolam. In vivo rat pharmacokinetic studies confirmed this lack of drug interaction.
Keywords: carbene; mechanism-based inhibition; methylenedioxyphenyl compounds; podophyllotoxin; time-dependent inhibition.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibition of CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 by podophyllotoxin: implication for clinical drug-drug interactions.J Biosci. 2011 Dec;36(5):879-85. doi: 10.1007/s12038-011-9143-9. J Biosci. 2011. PMID: 22116286
-
Roles of cytochrome P450 3A enzymes in the 2-hydroxylation of 1,4-cineole, a monoterpene cyclic ether, by rat and human liver microsomes.Xenobiotica. 2001 Oct;31(10):713-23. doi: 10.1080/00498250110065595. Xenobiotica. 2001. PMID: 11695850
-
Inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A4 by a pyrimidineimidazole: Evidence for complex heme interactions.Chem Res Toxicol. 2006 Dec;19(12):1650-9. doi: 10.1021/tx060198m. Chem Res Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 17173379
-
Development and validation of a LC-MS/MS method for the in vitro analysis of 1-hydroxymidazolam in human liver microsomes: application for determining CYP3A4 inhibition in complex matrix mixtures.Biomed Chromatogr. 2013 Sep;27(9):1107-16. doi: 10.1002/bmc.2913. Epub 2013 May 14. Biomed Chromatogr. 2013. PMID: 23674377
-
Mini-series: I. Basic science. Uncertainty and inaccuracy of predicting CYP-mediated in vivo drug interactions in the ICU from in vitro models: focus on CYP3A4.Intensive Care Med. 2009 Mar;35(3):417-29. doi: 10.1007/s00134-008-1384-1. Epub 2009 Jan 9. Intensive Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19132343 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of alcohol-induced increase in CYP2E1 content in human liver microsomes on the activity and cooperativity of CYP3A4.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021 Feb 15;698:108677. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108677. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 33197431 Free PMC article.
-
Time-dependent enzyme inactivation: Numerical analyses of in vitro data and prediction of drug-drug interactions.Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Feb;206:107449. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107449. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31836452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improved Predictions of Drug-Drug Interactions Mediated by Time-Dependent Inhibition of CYP3A.Mol Pharm. 2018 May 7;15(5):1979-1995. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00129. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29608318 Free PMC article.
-
Numerical Analysis of Time-Dependent Inhibition by MDMA.Drug Metab Dispos. 2020 Jan;48(1):1-7. doi: 10.1124/dmd.119.089268. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Drug Metab Dispos. 2020. PMID: 31641009 Free PMC article.
-
Irreversible Enzyme Inhibition Kinetics and Drug-Drug Interactions.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2342:51-88. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1554-6_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34272691
References
-
- Silverman R. Mechanism-based enzyme inactivators. Academic Press; San Diego: 1995. - PubMed
-
- de Montellano PRO, Correia MA. Cytochrome P450. Springer; 1995. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes; pp. 305–364.
-
- Orr ST, Ripp SL, Ballard TE, Henderson JL, Scott DO, Obach RS, Sun H, Kalgutkar AS. Mechanism-based inactivation (MBI) of cytochrome P450 enzymes: structure–activity relationships and discovery strategies to mitigate drug–drug interaction risks. Journal of medicinal chemistry. 2012;55(11):4896–4933. - PubMed
-
- Obach RS, Walsky RL, Venkatakrishnan K. Mechanism-based inactivation of human cytochrome P450 enzymes and the prediction of drug-drug interactions. Drug metabolism and disposition. 2007;35(2):246–255. - PubMed
-
- Grimm SW, Einolf HJ, Hall SD, He K, Lim HK, Ling KHJ, Lu C, Nomeir AA, Seibert E, Skordos KW. The conduct of in vitro studies to address time-dependent inhibition of drug-metabolizing enzymes: a perspective of the pharmaceutical research and manufacturers of America. Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 2009;37(7):1355–1370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

