Molecular Cloning of HbPR-1 Gene from Rubber Tree, Expression of HbPR-1 Gene in Nicotiana benthamiana and Its Inhibition of Phytophthora palmivora
- PMID: 27337148
- PMCID: PMC4940168
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157591
Molecular Cloning of HbPR-1 Gene from Rubber Tree, Expression of HbPR-1 Gene in Nicotiana benthamiana and Its Inhibition of Phytophthora palmivora
Abstract
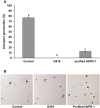
This is the first report to present a full-length cDNA (designated HbPR-1) encoding a putative basic HbPR-1 protein from rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) treated with salicylic acid. It was characterized and also expressed in Nicotiana benthamiana using Agrobacterium-mediated transient gene expression system in order to investigate the role of HbPR-1 gene in rubber tree against its oomycete pathogen Phytopthora palmivora and to produce recombinant HbPR-1 protein for microbial inhibition test. The HbPR-1 cDNA was 647 bp long and contained an open reading frame of 492 nucleotides encoding 163 amino acid residues with a predicted molecular mass of 17,681 Da and an isoelectric point (pI) of 8.56, demonstrating that HbPR-1 protein belongs to the basic PR-1 type. The predicted 3D structure of HbPR-1 was composed of four α-helices, three β-sheets, seven strands, and one junction loop. Expression and purification of recombinant HbPR-1 protein were successful using Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression and one-step of affinity chromatography. Heterologous expression of HbPR-1 in N. benthamiana reduced necrosis areas which were inoculated with P. palmivora zoospores, indicating that the expressed HbPR-1 protein played an important role in plant resistance to pathogens. The purified recombinant HbPR-1 protein was found to inhibit 64% of P. palmivora zoospore germination on a water agar plate compared with control, suggesting that it was an antimicrobial protein against P. palmivora.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
The plant defense and pathogen counterdefense mediated by Hevea brasiliensis serine protease HbSPA and Phytophthora palmivora extracellular protease inhibitor PpEPI10.PLoS One. 2017 May 1;12(5):e0175795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175795. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28459807 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and Expression Analysis of HbPR-1b and HbPR-3 in Hevea brasiliensis During Inoculation with Rigidoporus microporus.Pak J Biol Sci. 2017;20(5):233-243. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2017.233.243. Pak J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29023035
-
Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel bi-functional α-amylase/subtilisin inhibitor from Hevea brasiliensis.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016 Apr;101:76-87. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.01.014. Epub 2016 Jan 26. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26854410
-
Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of a novel cystatin from Hevea rubber latex.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2011 Mar;49(3):244-50. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.12.007. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21247772
-
Novel Cell Death-Inducing Elicitors from Phytophthora palmivora Promote Infection on Hevea brasiliensis.Phytopathology. 2019 Oct;109(10):1769-1778. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-01-19-0002-R. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Phytopathology. 2019. PMID: 31246138
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling of Pathogenesis-Related Protein 1 (PR-1) Genes in Durum Wheat (Triticum durum Desf.).Plants (Basel). 2023 May 16;12(10):1998. doi: 10.3390/plants12101998. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37653915 Free PMC article.
-
Sulphated Polysaccharide from Acanthophora spicifera Induced Hevea brasiliensis Defense Responses Against Phytophthora palmivora Infection.Plants (Basel). 2019 Mar 22;8(3):73. doi: 10.3390/plants8030073. Plants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30909469 Free PMC article.
-
The plant defense and pathogen counterdefense mediated by Hevea brasiliensis serine protease HbSPA and Phytophthora palmivora extracellular protease inhibitor PpEPI10.PLoS One. 2017 May 1;12(5):e0175795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175795. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28459807 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation-based gene silencing and functional characterization of an ISC effector reveal how a powdery mildew fungus disturbs salicylic acid biosynthesis and immune response in the plant.Mol Plant Pathol. 2024 Nov;25(11):e70030. doi: 10.1111/mpp.70030. Mol Plant Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39558488 Free PMC article.
-
A secreted protein of 15 kDa plays an important role in Phytophthora palmivora development and pathogenicity.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 11;10(1):2319. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59007-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32047196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sarowar S, Kim YJ, Kim EN, Kim KD, Hwang BK, Islam R, et al. Overexpression of a pepper basic pathogenesis-related protein 1 gene in tobacco plants enhances resistance to heavy metal and pathogen stresses. Plant Cell Rep. 2005; 24: 216–224. - PubMed
-
- Liu Q, Xue Q. Computational identification of novel PR-1-type genes in Oryza sativa. J. Genet. 2006; 85(3): 193–198. - PubMed
-
- Kim YJ, Hwang BK. Pepper gene encoding a basic pathogenesis-related 1 protein is pathogen and ethylene inducible. Physiol. plant. 2000; 108: 51–60.
-
- Yang RH, Tang K, Liu HT, Huang WD. Effect of salicylic acid on jasmonic acid- related defense response of pea seedlings to wounding. Sci. Hortic. 2011; 128: 166–173.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

