Antimicrobial Activity and Modulatory Effect of Essential Oil from the Leaf of Rhaphiodon echinus (Nees & Mart) Schauer on Some Antimicrobial Drugs
- PMID: 27338314
- PMCID: PMC6274211
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21060743
Antimicrobial Activity and Modulatory Effect of Essential Oil from the Leaf of Rhaphiodon echinus (Nees & Mart) Schauer on Some Antimicrobial Drugs
Abstract
Background: Rhaphiodon echinus is a weed plant used in the Brazilian folk medicinal for the treatment of infectious diseases. In this study, the essential oil of R. echinus leaf was investigated for its antimicrobial properties.
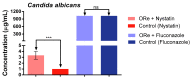
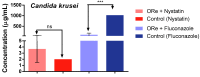
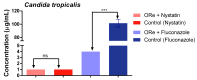
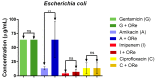
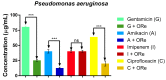
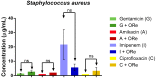
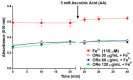
Methods: The chemical constituents of the essential oil were characterized by GC-MS. The antimicrobial properties were determined by studying by the microdilution method the effect of the oil alone, and in combination with antifungal or antibiotic drugs against the fungi Candida albicans, Candida krusei and Candida tropicalis and the microbes Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas. In addition, the iron (II) chelation potential of the oil was determined.
Results: The results showed the presence of β-caryophyllene and bicyclogermacrene in major compounds, and revealed a low antifungal and antibacterial activity of the essential oil, but a strong modulatory effect on antimicrobial drugs when associated with the oil. The essential oil showed iron (II) chelation activity.
Conclusions: The GC-MS characterization revealed the presence of monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes in the essential oil and metal chelation potential, which may be responsible in part for the modulatory effect of the oil. These findings suggest that essential oil of R. echinus is a natural product capable of enhancing the antibacterial and antifungal activity of antimicrobial drugs.
Keywords: R. echinus; antibacterial activity; antifungal activity; modulating; natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Salkovic-Petrisic M., Knezovic A., Osmanovic-Barilar J., Smailovic U., Trkulja V., Riederer P., Amit T., Mandel S., Youdim M.B.H. Multi-target iron-chelators improve memory loss in a rat model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2015;136:108–119. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.06.026. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barbosa Filho V.M., Waczuk E.P., Kamdem J.P., Abolaji A.O., Lacerda S.R., da Costa J.G.M., de Menezes I.R.A., Boligon A.A., Athayde M.L., da Rocha J.B.T. Phytochemical constituents, antioxidant activity, cytotoxicity and osmotic fragility effects of Caju (Anacardium microcarpum) Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014;55:280–288. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.02.021. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

