Natural Products to Counteract the Epidemic of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disorders
- PMID: 27338339
- PMCID: PMC4928700
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21060807
Natural Products to Counteract the Epidemic of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disorders
Abstract
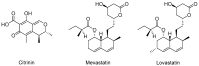
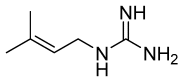
Natural products have always been exploited to promote health and served as a valuable source for the discovery of new drugs. In this review, the great potential of natural compounds and medicinal plants for the treatment or prevention of cardiovascular and metabolic disorders, global health problems with rising prevalence, is addressed. Special emphasis is laid on natural products for which efficacy and safety have already been proven and which are in clinical trials, as well as on plants used in traditional medicine. Potential benefits from certain dietary habits and dietary constituents, as well as common molecular targets of natural products, are also briefly discussed. A glimpse at the history of statins and biguanides, two prominent representatives of natural products (or their derivatives) in the fight against metabolic disease, is also included. The present review aims to serve as an "opening" of this special issue of Molecules, presenting key historical developments, recent advances, and future perspectives outlining the potential of natural products for prevention or therapy of cardiovascular and metabolic disease.
Keywords: biguanides; cardiovascular disease; coffee; diabetes mellitus; dietary constituents; metabolic disorders; molecular targets; natural products; statins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Atanasov A.G., Waltenberger B., Pferschy-Wenzig E.M., Linder T., Wawrosch C., Uhrin P., Temml V., Wang L., Schwaiger S., Heiss E.H., et al. Discovery and resupply of pharmacologically active plant-derived natural products: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015;33:1582–1614. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- David B., Wolfender J.-L., Dias D.A. The pharmaceutical industry and natural products: Historical status and new trends. Phytochem. Rev. 2015;14:299–315. doi: 10.1007/s11101-014-9367-z. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
