Functional Characterization of Soybean Glyma04g39610 as a Brassinosteroid Receptor Gene and Evolutionary Analysis of Soybean Brassinosteroid Receptors
- PMID: 27338344
- PMCID: PMC4926431
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17060897
Functional Characterization of Soybean Glyma04g39610 as a Brassinosteroid Receptor Gene and Evolutionary Analysis of Soybean Brassinosteroid Receptors
Abstract
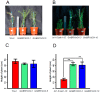
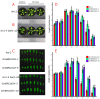
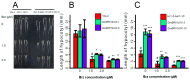
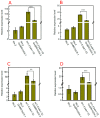
Brassinosteroids (BR) play important roles in plant growth and development. Although BR receptors have been intensively studied in Arabidopsis, the BR receptors in soybean remain largely unknown. Here, in addition to the known receptor gene Glyma06g15270 (GmBRI1a), we identified five putative BR receptor genes in the soybean genome: GmBRI1b, GmBRL1a, GmBRL1b, GmBRL2a, and GmBRL2b. Analysis of their expression patterns by quantitative real-time PCR showed that they are ubiquitously expressed in primary roots, lateral roots, stems, leaves, and hypocotyls. We used rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) to clone GmBRI1b (Glyma04g39160), and found that the predicted amino acid sequence of GmBRI1b showed high similarity to those of AtBRI1 and pea PsBRI1. Structural modeling of the ectodomain also demonstrated similarities between the BR receptors of soybean and Arabidopsis. GFP-fusion experiments verified that GmBRI1b localizes to the cell membrane. We also explored GmBRI1b function in Arabidopsis through complementation experiments. Ectopic over-expression of GmBRI1b in Arabidopsis BR receptor loss-of-function mutant (bri1-5 bak1-1D) restored hypocotyl growth in etiolated seedlings; increased the growth of stems, leaves, and siliques in light; and rescued the developmental defects in leaves of the bri1-6 mutant, and complemented the responses of BR biosynthesis-related genes in the bri1-5 bak1-D mutant grown in light. Bioinformatics analysis demonstrated that the six BR receptor genes in soybean resulted from three gene duplication events during evolution. Phylogenetic analysis classified the BR receptors in dicots and monocots into three subclades. Estimation of the synonymous (Ks) and the nonsynonymous substitution rate (Ka) and selection pressure (Ka/Ks) revealed that the Ka/Ks of BR receptor genes from dicots and monocots were less than 1.0, indicating that BR receptor genes in plants experienced purifying selection during evolution.
Keywords: BR receptor; brassinosteroids; evolution; gene family; soybean.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Evolutionary analysis and functional characterization of SiBRI1 as a Brassinosteroid receptor gene in foxtail millet.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jun 24;21(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03081-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34167462 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of the brassinosteroid receptor gene (GmBRI1) from Glycine max.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Mar 4;15(3):3871-88. doi: 10.3390/ijms15033871. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24599079 Free PMC article.
-
GmBZL3 acts as a major BR signaling regulator through crosstalk with multiple pathways in Glycine max.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Feb 22;19(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1677-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 30795735 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Lesions in BRI1 and Its Orthologs in the Plant Kingdom.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 25;25(15):8111. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158111. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ligand perception, activation, and early signaling of plant steroid receptor brassinosteroid insensitive 1.J Integr Plant Biol. 2013 Dec;55(12):1198-211. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12081. Epub 2013 Sep 9. J Integr Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23718739 Review.
Cited by
-
Brassinosteroid biosynthesis and signaling: Conserved and diversified functions of core genes across multiple plant species.Plant Commun. 2024 Sep 9;5(9):100982. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2024.100982. Epub 2024 May 29. Plant Commun. 2024. PMID: 38816993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ectopic expression of GmNF-YA8 in Arabidopsis delays flowering via modulating the expression of gibberellic acid biosynthesis- and flowering-related genes and promotes lateral root emergence in low phosphorus conditions.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 20;13:1033938. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1033938. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36340418 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal Brassinosteroid Levels Are Required for Soybean Growth and Mineral Nutrient Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 5;22(16):8400. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168400. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445112 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary analysis and functional characterization of SiBRI1 as a Brassinosteroid receptor gene in foxtail millet.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jun 24;21(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03081-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34167462 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Characterization of the Steroid Reductase Genes GmDET2a and GmDET2b form Glycine max.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 3;19(3):726. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030726. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29510512 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

