Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Spirulina platensis Extract via the Modulation of Histone Deacetylases
- PMID: 27338466
- PMCID: PMC4924221
- DOI: 10.3390/nu8060381
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Spirulina platensis Extract via the Modulation of Histone Deacetylases
Abstract
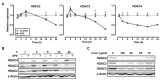
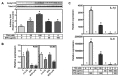
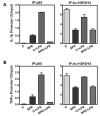
We previously demonstrated that the organic extract of Spirulina platensis (SPE), an edible blue-green alga, possesses potent anti-inflammatory effects. In this study, we investigated if the regulation of histone deacetylases (HDACs) play a role in the anti-inflammatory effect of SPE in macrophages. Treatment of macrophages with SPE rapidly and dose-dependently reduced HDAC2, 3, and 4 proteins which preceded decreases in their mRNA levels. Degradation of HDAC4 protein was attenuated in the presence of inhibitors of calpain proteases, lysosomal acidification, and Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, respectively, but not a proteasome inhibitor. Acetylated histone H3 was increased in SPE-treated macrophages to a similar level as macrophages treated with a pan-HDAC inhibitor, with concomitant inhibition of inflammatory gene expression upon LPS stimulation. Knockdown of HDAC3 increased basal and LPS-induced pro-inflammatory gene expression, while HDAC4 knockdown increased basal expression of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), but attenuated LPS-induced inflammatory gene expression. Chromatin immunoprecipitation showed that SPE decreased p65 binding and H3K9/K14 acetylation at the Il-1β and tumor necrosis factor α (Tnfα) promoters. Our results suggest that SPE increased global histone H3 acetylation by facilitating HDAC protein degradation, but decreases histone H3K9/K14 acetylation and p65 binding at the promoters of Il-1β and Tnfα to exert its anti-inflammatory effect.
Keywords: Spirulina platensis; anti-inflammatory; epigenetics; histone deacetylases; inflammation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Edible blue-green algae reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting NF-κB pathway in macrophages and splenocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Apr;1830(4):2981-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.01.018. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23357040 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Spirulina platensis in Macrophages Is Beneficial for Adipocyte Differentiation and Maturation by Inhibiting Nuclear Factor-κB Pathway in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes.J Med Food. 2016 Jun;19(6):535-42. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2015.0156. Epub 2016 May 20. J Med Food. 2016. PMID: 27206252 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of an Endotoxin Tolerance-Like Mechanism for the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Spirulina platensis Organic Extract in Macrophages.J Med Food. 2017 Mar;20(3):201-210. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2016.0119. Epub 2017 Jan 25. J Med Food. 2017. PMID: 28121488
-
Histone deacetylases and their inhibitors in inflammatory diseases.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Oct;179:117295. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117295. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39146765 Review.
-
Role of redox signaling, protein phosphatases and histone acetylation in the inflammatory cascade in acute pancreatitis. Therapeutic implications.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2010 Jun;9(2):97-108. doi: 10.2174/187152810791292773. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20361855 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Arthrospira maxima Phycobiliproteins, Rosiglitazone, and 17β-Estradiol on Lipogenic and Inflammatory Gene Expression during 3T3-L1 Preadipocyte Cell Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 10;25(14):7566. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147566. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062809 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Spirulina platensis and ascorbic acid on amikacin-induced nephrotoxicity in rabbits.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Mar;26(8):8080-8086. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04249-4. Epub 2019 Jan 26. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30685861
-
Improved HDAC Inhibition, Stronger Cytotoxic Effect and Higher Selectivity against Leukemias and Lymphomas of Novel, Tricyclic Vorinostat Analogues.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Aug 26;14(9):851. doi: 10.3390/ph14090851. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34577551 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Allosteric Hydrazide-Containing Class I Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors for Use in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.J Med Chem. 2016 Nov 10;59(21):9942-9959. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01385. Epub 2016 Oct 26. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27754681 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of C-Phycocyanin on Microglia Activation Is Mediated by Toll-like Receptor 4.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 27;23(3):1440. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031440. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Halili M.A., Andrews M.R., Labzin L.I., Schroder K., Matthias G., Cao C., Lovelace E., Reid R.C., Le G.T., Hume D.A., et al. Differential effects of selective hdac inhibitors on macrophage inflammatory responses to the toll-like receptor 4 agonist lps. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010;87:1103–1114. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0509363. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

