BTG4, a maternal mRNA cleaner
- PMID: 27339058
- PMCID: PMC4991668
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjw031
BTG4, a maternal mRNA cleaner
Figures
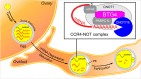
Comment on
-
BTG4 is a meiotic cell cycle-coupled maternal-zygotic-transition licensing factor in oocytes.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016 May;23(5):387-94. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3204. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27065194
-
BTG4 is a key regulator for maternal mRNA clearance during mouse early embryogenesis.J Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Aug;8(4):366-8. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjw023. Epub 2016 May 17. J Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27190313 No abstract available.
References
-
- Giraldez A.J., Mishima Y., Rihel J., et al. (2006). Zebrafish MiR-430 promotes deadenylation and clearance of maternal mRNAs. Science 312, 75–79. - PubMed
-
- He L., and Hannon G.J. (2004). MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 522–531. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y., Lu X., Shi J., et al. (2016). BTG4 is a key regulator for maternal mRNA clearance during mouse early embryogenesis. J. Mol. Cell Biol. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjw023. - PubMed
-
- Ramos S.B., Stumpo D.J., Kennington E.A., et al. (2004). The CCCH tandem zinc-finger protein Zfp36l2 is crucial for female fertility and early embryonic development. Development 131, 4883–4893. - PubMed
-
- Semotok J.L., Cooperstock R.L., Pinder B.D., et al. (2005). Smaug recruits the CCR4/POP2/NOT deadenylase complex to trigger maternal transcript localization in the early Drosophila embryo. Curr. Biol. 15, 284–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

