Reprogramming of avian neural crest axial identity and cell fate
- PMID: 27339986
- PMCID: PMC5100669
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaf2729
Reprogramming of avian neural crest axial identity and cell fate
Abstract
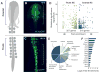
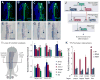
Neural crest populations along the embryonic body axis of vertebrates differ in developmental potential and fate, so that only the cranial neural crest can contribute to the craniofacial skeleton in vivo. We explored the regulatory program that imbues the cranial crest with its specialized features. Using axial-level specific enhancers to isolate and perform genome-wide profiling of the cranial versus trunk neural crest in chick embryos, we identified and characterized regulatory relationships between a set of cranial-specific transcription factors. Introducing components of this circuit into neural crest cells of the trunk alters their identity and endows these cells with the ability to give rise to chondroblasts in vivo. Our results demonstrate that gene regulatory circuits that support the formation of particular neural crest derivatives may be used to reprogram specific neural crest-derived cell types.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures


References
-
- Le Douarin N. The neural crest. Cambridge University Press; 1982.
-
- Dyachuk V, et al. Parasympathetic neurons originate from nerve associated peripheral glial progenitors. Science. 2014;345:82–87. - PubMed
-
- Le Lievre CS, Le Douarin NM. Mesenchymal derivatives of the neural crest: analysis of chimaeric quail and chick embryos. Journal of embryology and experimental morphology. 1975;34:125–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

