Inflammation and Progression of CKD: The CRIC Study
- PMID: 27340285
- PMCID: PMC5012490
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.13121215
Inflammation and Progression of CKD: The CRIC Study
Abstract
Background and objectives: CKD is a global public health problem with significant mortality and morbidity.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We examined the multivariable association of plasma levels of IL-1, IL-1 receptor antagonist, IL-6, TNF-α, TGF-β, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, and serum albumin with progression of CKD in 3430 Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort study participants.
Results: Over a median follow-up time of 6.3 years, 899 participants reached the composite end point of ≥50% decline in eGFR from baseline or onset of ESRD. Elevated plasma levels of fibrinogen, IL-6, and TNF-α and lower serum albumin were associated with a greater decline in eGFR over time. After adjusting for demographics, BP, laboratory variables, medication use, and baseline eGFR, hazard ratios for the composite outcome were greater for the patients in the highest quartile of fibrinogen (hazard ratio, 2.05; 95% confidence interval, 1.64 to 2.55; P<0.001), IL-6 (hazard ratio, 1.44; 95% confidence interval, 1.17 to 1.77; P<0.01), and TNF-α (hazard ratio, 1.94; 95% confidence interval, 1.52 to 2.47; P<0.001) compared with those in the respective lowest quartiles. The hazard ratio was 3.48 (95% confidence interval, 2.88 to 4.21; P<0.001) for patients in the lowest serum albumin quartile relative to those in the highest quartile. When also adjusted for albuminuria, the associations of fibrinogen (hazard ratio, 1.49; 95% confidence interval, 1.20 to 1.86; P<0.001), serum albumin (hazard ratio, 1.52; 95% confidence interval, 1.24 to 1.87; P<0.001), and TNF-α (hazard ratio, 1.42; 95% confidence interval, 1.11 to 1.81; P<0.001) with outcome were attenuated but remained significant.
Conclusions: Elevated plasma levels of fibrinogen and TNF-α and decreased serum albumin are associated with rapid loss of kidney function in patients with CKD.
Keywords: C-Reactive Protein; Follow-Up Studies; Humans; Inflammation; Interleukin-6; Renal Insufficiency, Chronic; Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha; albuminuria; chronic kidney disease; cytokines; end-stage renal disease; glomerular filtration rate.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
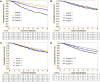


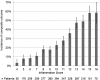
References
-
- United States Renal Data System : Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States, Bethesda, MD, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2012
-
- Gilbertson DT, Liu J, Xue JL, Louis TA, Solid CA, Ebben JP, Collins AJ: Projecting the number of patients with end-stage renal disease in the United States to the year 2015. J Am Soc Nephrol 16: 3736–3741, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Anderson GF, Chu E: Expanding priorities--confronting chronic disease in countries with low income. N Engl J Med 356: 209–211, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Nath KA: Tubulointerstitial changes as a major determinant in the progression of renal damage. Am J Kidney Dis 20: 1–17, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Yu HT: Progression of chronic renal failure. Arch Intern Med 163: 1417–1429, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072231/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001878/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103337/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK099924/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK099914/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073665/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

