Replacement of Vertebral Lamina (Laminoplasty) in Surgery for Lumbar Isthmic Spondylolisthesis: 5-Year Follow-Up Results
- PMID: 27340522
- PMCID: PMC4917761
- DOI: 10.4184/asj.2016.10.3.443
Replacement of Vertebral Lamina (Laminoplasty) in Surgery for Lumbar Isthmic Spondylolisthesis: 5-Year Follow-Up Results
Abstract
Study design: A review of clinical and radiological outcomes of lumbar laminoplasty (LL) for the treatment of isthmic spondylolisthesis (ISL).
Purpose: The single session performance of posterior lumbar interbody fusion with allograft in the anterior column and providing the realignment of the vertebrae was presented as a preliminary report earlier.
Overview of literature: Long-term surgical outcome of cervical laminoplasty in patients has been reported. But, outcome of LL in patients is unclear.
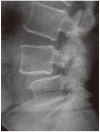
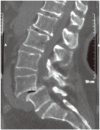
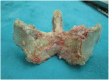
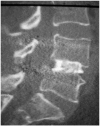
Methods: The long-term (5 years) year follow-up results of the LL technique are reported in this retrospective study. All patients underwent preoperative and postoperative direct X-ray, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging. The patients that did not respond to conservative treatment were operated. Twenty-one (52.5%) female and 19 (47.5%) male patients were included.
Results: Mean age was 43,5 years (ranges, 22-57 years). The most common symptoms were low back pain (89%), pelvic and leg pain (69%) and reduction in walking distance (65%). A total of 180 pedicle screws were inserted in 40 patients; posterior lumbar interbody fusion and laminoplasty with reduction was performed in 20 patients for L4-L5, 12 patients for L5-S1, 4 patients for L3-L4-L5 and 4 patients for L4-L5-S1. Ten (25%) patients with ILL had accompanying spinal stenosis. The difference between preoperative and postoperative sagittal plane rotation and dislocation degrees and disc space heights were statistically significant in all patients (p<0.05). Solid grade 4 fusion was observed in 38 patients; in only 2 patients grade 2 pseudoarthrosis developed (5%), but these patients were asymptomatic. Visual analog scale, Prolo economical and functional scale was examined with an average follow-up 5.5 years.
Conclusions: LL technique has the advantages of shorter duration of operation, lack of graft donor site complications, protection of posterior column osseoligamentous structures and achievement of high fusion rates in one session.
Keywords: Follow up studies; Isthmic spondylolisthesis; Laminoplasty; Long term; Lumbar; Posterior fusion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

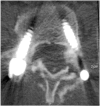
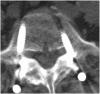
References
-
- Moller H, Hedlund R. Instrumented and noninstrumented posterolateral fusion in adult spondylolisthesis--a prospective randomized study: part 2. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000;25:1716–1721. - PubMed
-
- Benini A, Plotz G. Reduction and stabilization without laminectomy for unstable degenerative spondylolisthesis: a preliminary report. Neurosurgery. 1995;37:843–844. - PubMed
-
- Fraser RD. Interbody, posterior, and combined lumbar fusions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1995;20:167S–177S. - PubMed
-
- Matsudaira K, Yamazaki T, Seichi A, et al. Spinal stenosis in grade I degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: a comparative study of outcomes following laminoplasty and laminectomy with instrumented spinal fusion. J Orthop Sci. 2005;10:270–276. - PubMed
-
- Sears W. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lytic spondylolisthesis: restoration of sagittal balance using insert-and-rotate interbody spacers. Spine J. 2005;5:161–169. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

