Hypophosphatemic Rickets in Siblings: A Rare Case Report
- PMID: 27340574
- PMCID: PMC4906197
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/4803167
Hypophosphatemic Rickets in Siblings: A Rare Case Report
Abstract
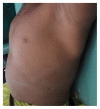
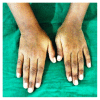
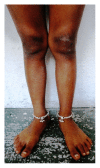
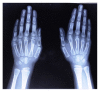
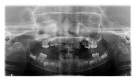
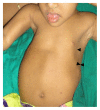
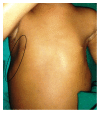
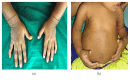
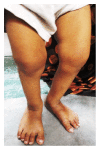
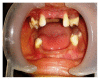
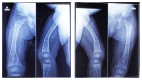
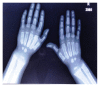
Hypophosphatemic rickets (HR) is a type of hereditary rickets characterized by persistent hypophosphatemia and hyperphosphaturia. The most predominant type is inherited in an X-linked fashion and caused by mutation in the gene encoding the phosphate-regulating endopeptidase homolog, X-linked (PHEX), identified in 1995. The X-linked hypophosphatemic (XLH) rickets is a rare hereditary metabolic disorder with a prevalence of 1 in 20,000 and causes deficient calcification of mineralized structures such as bones and teeth resulting in dental problems in terms of delayed eruption, spontaneous periapical infections, and exfoliation. We report one such unique case of hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets in siblings exhibiting classical features of rickets with emphasis on its treatment and dental considerations.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A PHEX gene mutation is responsible for adult-onset vitamin D-resistant hypophosphatemic osteomalacia: evidence that the disorder is not a distinct entity from X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998 Oct;83(10):3459-62. doi: 10.1210/jcem.83.10.5167. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998. PMID: 9768646
-
Pulp chamber features, prevalence of abscesses, disease severity, and PHEX mutation in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets.J Bone Miner Metab. 2021 Mar;39(2):212-223. doi: 10.1007/s00774-020-01136-8. Epub 2020 Aug 8. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021. PMID: 32772199
-
A Novel PHEX Mutation in Japanese Patients with X-Linked Hypophosphatemic Rickets.Case Rep Genet. 2015;2015:301264. doi: 10.1155/2015/301264. Epub 2015 Mar 15. Case Rep Genet. 2015. PMID: 25861491 Free PMC article.
-
[Hereditary hypophosphatemia in adults].Presse Med. 2005 Dec 17;34(22 Pt 1):1720-6. doi: 10.1016/s0755-4982(05)84260-5. Presse Med. 2005. PMID: 16374396 Review. French.
-
Phosphate homeostasis and genetic mutations of familial hypophosphatemic rickets.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Sep;28(9-10):1009-17. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2014-0366. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 25894638 Review.
Cited by
-
X-Linked Familial Hypophosphatemia: A Case Report of 27-Year Old Male and Review of Literature.Horm Metab Res. 2023 Oct;55(10):653-664. doi: 10.1055/a-2159-8429. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Horm Metab Res. 2023. PMID: 37813097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Misdiagnosed metabolic bone abnormality: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2023 Oct 20;17(1):436. doi: 10.1186/s13256-023-04164-w. J Med Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37858137 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D-Resistant Rickets Diagnostics and Treatment Challenges at Muhimbili National Hospital, Tanzania.Case Rep Endocrinol. 2020 Jan 28;2020:1547170. doi: 10.1155/2020/1547170. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32082647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hernández G. G., Laguna F. B. Dental characteristics of hypophosphatemic rickets. Case report. Revista Odontológica Mexicana. 2013;17(2):101–108.
-
- Econs M. J., Francis F. Positional cloning of the PEX gene: new insights into the pathophysiology of X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. American Journal of Physiology—Renal Physiology. 1997;273(4):F489–F498. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

