Hypophosphatemic Rickets in Siblings: A Rare Case Report
- PMID: 27340574
- PMCID: PMC4906197
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/4803167
Hypophosphatemic Rickets in Siblings: A Rare Case Report
Abstract
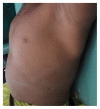
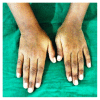
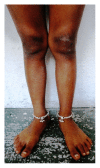
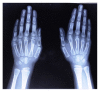
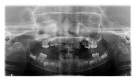
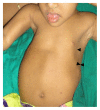
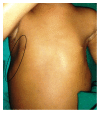
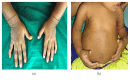
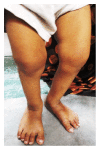
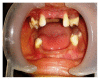
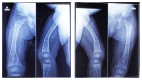
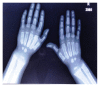
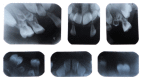
Hypophosphatemic rickets (HR) is a type of hereditary rickets characterized by persistent hypophosphatemia and hyperphosphaturia. The most predominant type is inherited in an X-linked fashion and caused by mutation in the gene encoding the phosphate-regulating endopeptidase homolog, X-linked (PHEX), identified in 1995. The X-linked hypophosphatemic (XLH) rickets is a rare hereditary metabolic disorder with a prevalence of 1 in 20,000 and causes deficient calcification of mineralized structures such as bones and teeth resulting in dental problems in terms of delayed eruption, spontaneous periapical infections, and exfoliation. We report one such unique case of hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets in siblings exhibiting classical features of rickets with emphasis on its treatment and dental considerations.
Figures






References
-
- Hernández G. G., Laguna F. B. Dental characteristics of hypophosphatemic rickets. Case report. Revista Odontológica Mexicana. 2013;17(2):101–108.
-
- Econs M. J., Francis F. Positional cloning of the PEX gene: new insights into the pathophysiology of X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. American Journal of Physiology—Renal Physiology. 1997;273(4):F489–F498. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

