Sulfasalazine-induced renal and hepatic injury in rats and the protective role of taurine
- PMID: 27340618
- PMCID: PMC4916549
- DOI: 10.15171/bi.2016.01
Sulfasalazine-induced renal and hepatic injury in rats and the protective role of taurine
Abstract
Introduction: Sulfasalazine is a drug commonly administrated against inflammatory-based disorders. On the other hand, kidney and liver injury are serious adverse events accompanied by sulfasalazine administration. No specific therapeutic option is available against this complication. The current investigation was designed to evaluate the potential protective effects of taurine against sulfasalazine-induced kidney and liver injury in rats.
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were administered with sulfasalazine (600 mg/kg, oral) for 14 consecutive days. Animals received different doses of taurine (250, 500 and 1000 mg/ kg, i.p.) every day. Markers of organ injury were evaluated on day 15(th), 24 h after the last dose of sulfasalazine.
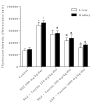
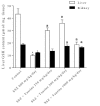
Results: Sulfasalazine caused renal and hepatic injury as judged by an increase in serum level of creatinine (Cr), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP). The levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid peroxidation were raised in kidney and liver of sulfasalazine-treated animals. Moreover, tissue glutathione reservoirs were depleted after sulfasalazine administration. Histopathological changes of kidney and liver also endorsed organ injury. Taurine administration (250, 500 and 1000 mg/kg/day, i.p) alleviated sulfasalazine-induced renal and hepatic damage.
Conclusion: Taurine administration could serve as a potential protective agent with therapeutic capabilities against sulfasalazine adverse effects.
Keywords: Anti-rheumatoid drugs; Drug-induced liver injury; Hepatotoxicity; Renal injury; Taurine.
Similar articles
-
Sulfasalazine-induced renal injury in rats and the protective role of thiol-reductants.Ren Fail. 2016;38(1):137-41. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2015.1096731. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Ren Fail. 2016. PMID: 26479898
-
Effect of Thiol-reducing Agents and Antioxidants on Sulfasalazine-induced Hepatic Injury in Normotermic Recirculating Isolated Perfused Rat Liver.Toxicol Res. 2016 Apr;32(2):133-40. doi: 10.5487/TR.2016.32.2.133. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Toxicol Res. 2016. PMID: 27123164 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfasalazine induces mitochondrial dysfunction and renal injury.Ren Fail. 2017 Nov;39(1):745-753. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2017.1399908. Ren Fail. 2017. PMID: 29214868 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigation of Methimazole-Induced Hepatic Injury by Taurine in Mice.Sci Pharm. 2014 Sep 30;83(1):143-58. doi: 10.3797/scipharm.1408-04. Print 2015 Jan-Mar. Sci Pharm. 2014. PMID: 26839807 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Mentha piperita L. leaf essential oil against CCl4 induced hepatic oxidative damage and renal failure in rats.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jan 9;17(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0645-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29316974 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Taurine Improves Sperm Mitochondrial Indices, Blunts Oxidative Stress Parameters, and Enhances Steroidogenesis and Kinematics of Sperm in Lead-Exposed Mice.Reprod Sci. 2023 Jun;30(6):1891-1910. doi: 10.1007/s43032-022-01140-5. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 36484981
-
A narrative review and new insights into the protective effects of taurine against drug side effects.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jan;398(1):203-230. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03331-0. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39141023 Review.
-
Protective antioxidative and anti-inflammatory actions of β-caryophyllene against sulfasalazine-induced nephrotoxicity in rat.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Apr;247(8):691-699. doi: 10.1177/15353702211073804. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 35068213 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic encephalopathy complications are diminished by piracetam via the interaction between mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and locomotor activity.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 29;9(10):e20557. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20557. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37810869 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress are involved in the mechanism of tramadol-induced renal injury.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021 Sep 3;2:100049. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100049. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34909675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corea N. Sulfasalazine. In: Enna SJ, Bylund DB, eds. xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference. New York: Elsevier; 2007:1-5.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources