Morphologic Damage of Rat Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells Induced by Bile Acids Could Be Ameliorated by Farnesoid X Receptor Inhibitor Z-Guggulsterone In Vitro
- PMID: 27340672
- PMCID: PMC4908247
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9283204
Morphologic Damage of Rat Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells Induced by Bile Acids Could Be Ameliorated by Farnesoid X Receptor Inhibitor Z-Guggulsterone In Vitro
Abstract
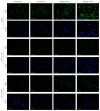
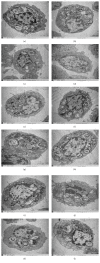
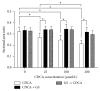
Objective. To determine whether bile acids (BAs) affect respiratory functions through the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) expressed in the lungs and to explore the possible mechanisms of BAs-induced respiratory disorder. Methods. Primary cultured alveolar epithelial type II cells (AECIIs) of rat were treated with different concentrations of chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) in the presence or absence of FXR inhibitor Z-guggulsterone (GS). Then, expression of FXR in nuclei of AECIIs was assessed by immunofluorescence microscopy. And ultrastructural changes of the cells were observed under transmission electron microscope and analyzed by Image-Pro Plus software. Results. Morphologic damage of AECIIs was exhibited in high BAs group in vitro, with high-level expression of FXR, while FXR inhibitor GS could attenuate the cytotoxicity of BAs to AECIIs. Conclusions. FXR expression was related to the morphologic damage of AECIIs induced by BAs, thus influencing respiratory functions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chenodeoxycholic Acid Releases Proinflammatory Cytokines from Small Intestinal Epithelial Cells Through the Farnesoid X Receptor.Digestion. 2019;100(4):286-294. doi: 10.1159/000496687. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Digestion. 2019. PMID: 30844798
-
Effects of bile acids and the bile acid receptor FXR agonist on the respiratory rhythm in the in vitro brainstem medulla slice of neonatal Sprague-Dawley rats.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 18;9(11):e112212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112212. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25405617 Free PMC article.
-
Bile acids induce activation of alveolar epithelial cells and lung fibroblasts through farnesoid X receptor-dependent and independent pathways.Respirology. 2016 Aug;21(6):1075-80. doi: 10.1111/resp.12815. Epub 2016 May 17. Respirology. 2016. PMID: 27185272
-
[Progress in the ligands and their complex structures of farnesoid X receptor].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012 Jun;47(6):704-15. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22919716 Review. Chinese.
-
Therapeutic effects of guggul and its constituent guggulsterone: cardiovascular benefits.Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2007 Winter;25(4):375-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2007.00023.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2007. PMID: 18078436 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Farnesoid X Receptor in the Pathogenesis of Respiratory Diseases.Can Respir J. 2020 Nov 26;2020:9137251. doi: 10.1155/2020/9137251. eCollection 2020. Can Respir J. 2020. PMID: 33294085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperoxia induces alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis by regulating mitochondrial function through small mothers against decapentaplegic 3 (SMAD3) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2).Bioengineered. 2022 Jan;13(1):242-252. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2012953. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 34898379 Free PMC article.
-
Farnesoid X receptor regulates lung macrophage activation and injury following nitrogen mustard exposure.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 1;454:116208. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2022.116208. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35998709 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

