Immunoregulatory effects triggered by immunobiotic Lactobacillus jensenii TL2937 strain involve efficient phagocytosis in porcine antigen presenting cells
- PMID: 27342653
- PMCID: PMC4921007
- DOI: 10.1186/s12865-016-0160-1
Immunoregulatory effects triggered by immunobiotic Lactobacillus jensenii TL2937 strain involve efficient phagocytosis in porcine antigen presenting cells
Abstract
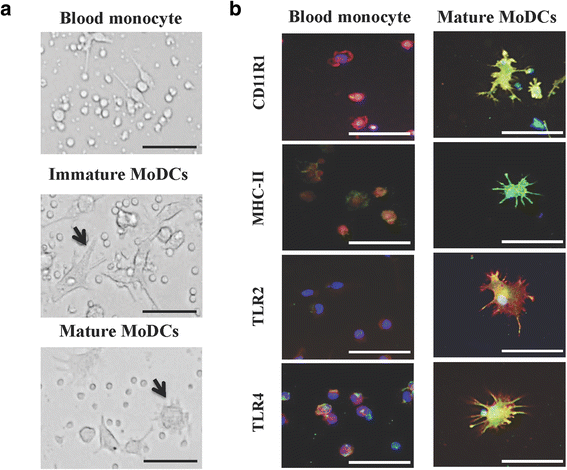
Background: Immunobiotic Lactobacillus jensenii TL2937 modulates porcine mononuclear phagocytes from Peyer's patches (PPMPs) and induces a differential production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in response to Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 activation. In view of the important role played by phagocytosis in the activation of antigen presenting cells (APCs), the aim of the present work was to examine the interaction of TL2937 with porcine PPMPs focusing on phagocytosis. In addition, this study aimed to investigate whether the effects of L. jensenii TL2937 in porcine blood monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MoDCs) are similar to those found in PPMPs considering that MoDCs do not recapitulate all functions of mucosal APCs.
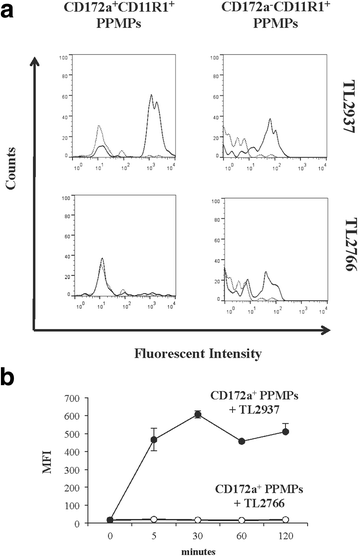
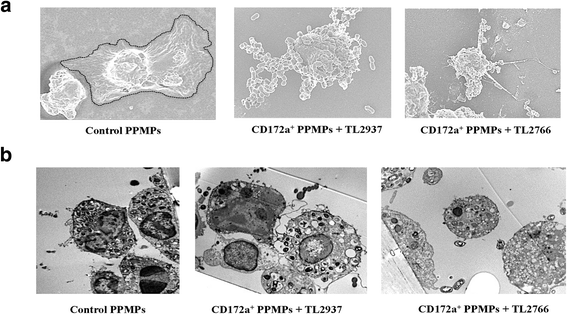
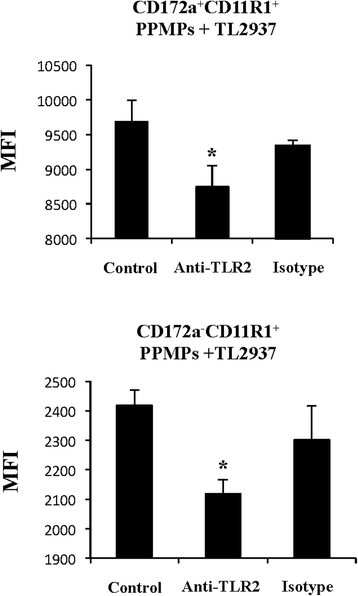
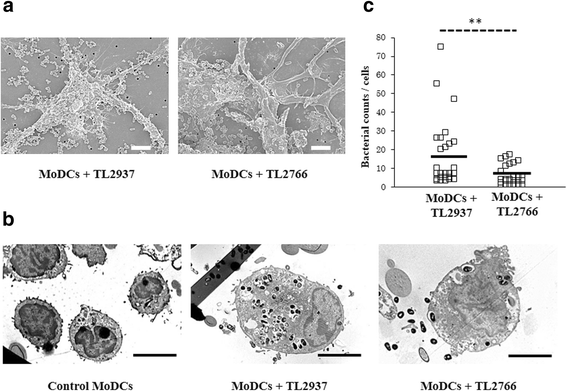
Results: Studies showed a high ability of porcine CD172a(+) PPMPs to phagocytose L. jensenii TL2937. Interestingly, our results also revealed a reduced capacity of the non-immunomodulatory L. plantarum TL2766 to be phagocytosed by those immune cells. Phagocytosis of L. jensenii TL2937 by porcine PPMPs was partially dependent on TLR2. In addition, we demonstrated that TL2937 strain was able to improve the expression of IL-1β, IL-12 and IL-10 in immature MoDCs resembling the effect of this immunobiotic bacterium on PPMPs. Moreover, similarly to PPMPs those immunomodulatory effects were related to the higher capacity of TL2937 to be phagocytosed by immature MoDCs.
Conclusions: Microbial recognition in APCs could be effectively mediated through ligand-receptor interactions that then mediate phagocytosis and signaling. For the immunobiotic strain TL2937, TLR2 has a partial role for its interaction with porcine APCs and it is necessary to investigate the role of other receptors. A challenge for future research will be advance in the full understanding of the molecular interactions of immunobiotic L. jensenii TL2937 with porcine APCs that will be crucial for the successful development of functional feeds for the porcine host. This study is a step in that direction.
Keywords: Blood monocytes-derived dendritic cells; Immunobiotics; Lactobacillus jensenii; Porcine antigen presenting cells.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

