Epidemic Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain among Belgian cystic fibrosis patients and review of literature
- PMID: 27342812
- PMCID: PMC4919866
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-016-0736-1
Epidemic Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain among Belgian cystic fibrosis patients and review of literature
Abstract
Background: Achromobacter xylosoxidans is increasingly being recognized as an emerging pathogen in cystic fibrosis. Recent severe infections with A. xylosoxidans in some of our cystic fibrosis (CF) patients led to a re-evaluation of the epidemiology of CF-associated A. xylosoxidans infections in two Belgian reference centres (Antwerp and Ghent). Several of these patients also stayed at the Rehabilitation Centre De Haan (RHC). In total, 59 A. xylosoxidans isolates from 31 patients (including 26 CF patients), collected between 2001 and 2014, were studied. We evaluated Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionisation -Time of Flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF) as an alternative for McRAPD typing.
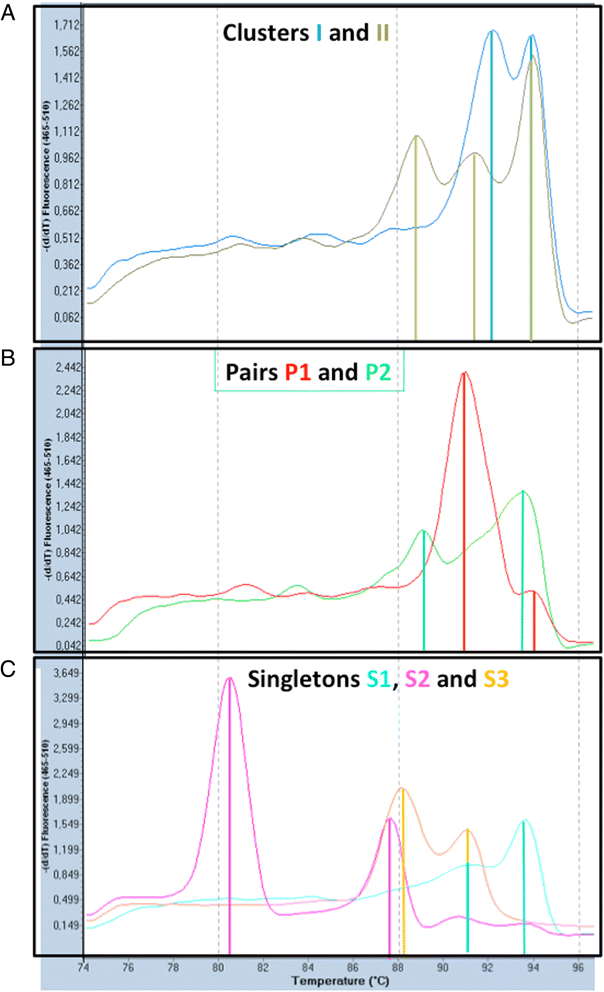
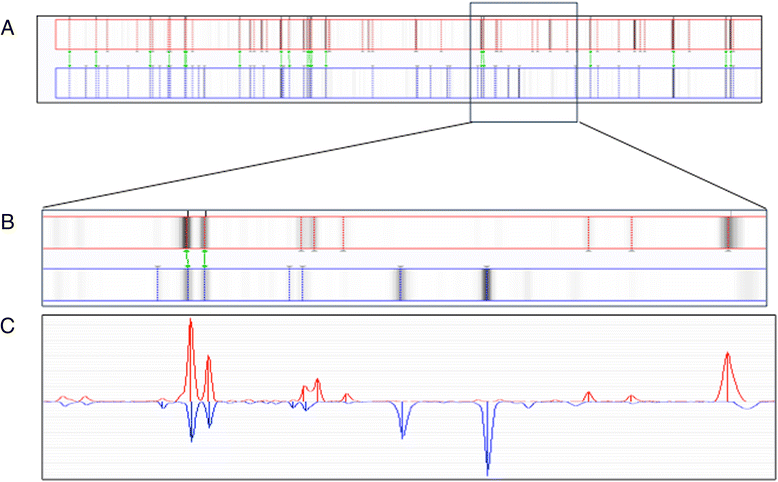
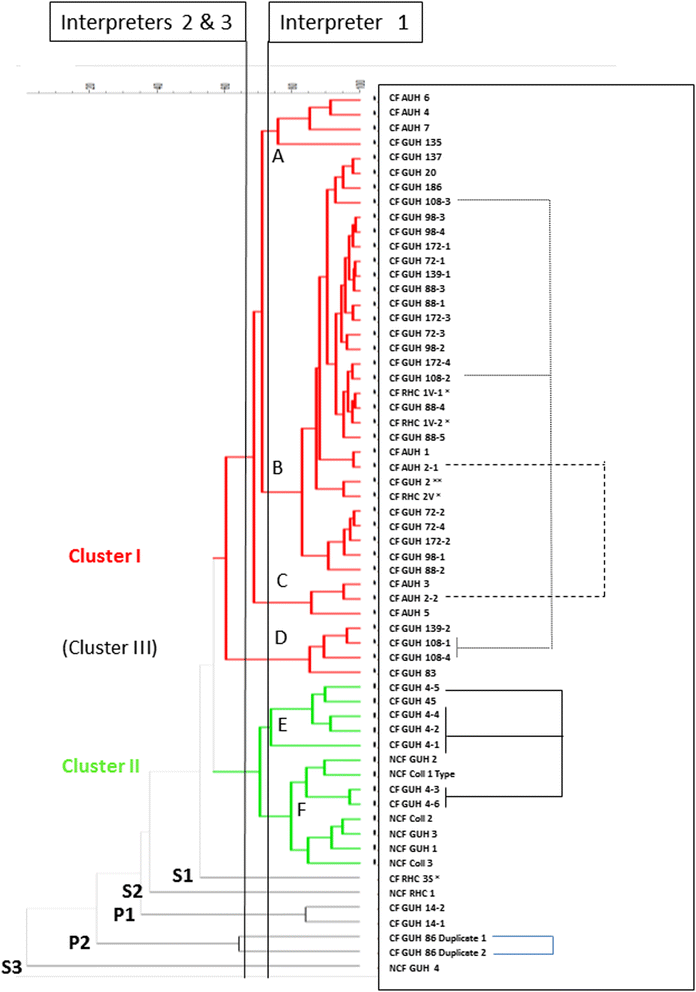
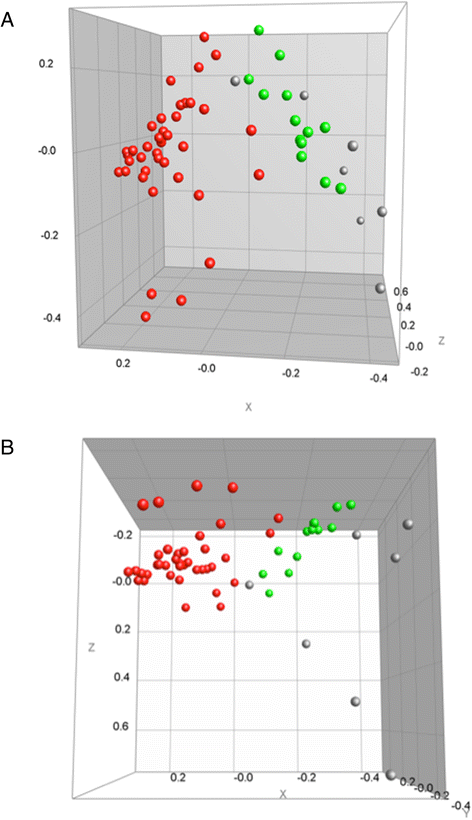
Results: Both typing approaches established the presence of a major cluster, comprising isolates, all from 21 CF patients, including from two patients sampled when staying at the RHC a decade ago. This major cluster was the same as the cluster established already a decade ago at the RHC. A minor cluster consisted of 13 isolates from miscellaneous origin. A further seven isolates, including one from a non-CF patient who had stayed recently at the RHC, were singletons.
Conclusions: Typing results of both methods were similar, indicating transmission of a single clone of A. xylosoxidans among several CF patients from at least two reference centres. Isolates of the same clone were already observed at the RHC, a decade ago. It is difficult to establish to what extent the RHC is the source of transmission, because the epidemic strain was already present when the first epidemiological study in the RHC was carried out. This study also documents the applicability of MALDI-TOF for typing of strains within the species A. xylosoxidans and the need to use the dynamic cutoff algorithm of the BioNumerics® software for correct clustering of the fingerprints.
Keywords: Achromobacter xylosoxidans; Cystic fibrosis; Epidemic strain; MALDI-TOF MS typing; McRAPD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Achromobacter xylosoxidans and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Emerging Pathogens Well-Armed for Life in the Cystic Fibrosis Patients' Lung.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 21;12(5):610. doi: 10.3390/genes12050610. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distribution of the species of Achromobacter in a French Cystic Fibrosis Centre and multilocus sequence typing analysis reveal the predominance of A. xylosoxidans and clonal relationships between some clinical and environmental isolates.J Cyst Fibros. 2016 Jul;15(4):486-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2015.12.009. Epub 2016 Jan 8. J Cyst Fibros. 2016. PMID: 26778615
-
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry for Rapid Detection of Isolates Belonging to the Epidemic Clones Achromobacter xylosoxidans ST137 and Achromobacter ruhlandii DES from Cystic Fibrosis Patients.J Clin Microbiol. 2021 Sep 20;59(10):e0094621. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00946-21. Epub 2021 Aug 4. J Clin Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34346714 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization for rapid identification of Achromobacter xylosoxidans and Alcaligenes faecalis recovered from cystic fibrosis patients.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Sep;44(9):3415-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00508-06. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16954289 Free PMC article.
-
Achromobacter spp. prevalence and adaptation in cystic fibrosis lung infection.Microbiol Res. 2022 Oct;263:127140. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127140. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Microbiol Res. 2022. PMID: 35931003 Review.
Cited by
-
Achromobacter xylosoxidans and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Emerging Pathogens Well-Armed for Life in the Cystic Fibrosis Patients' Lung.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 21;12(5):610. doi: 10.3390/genes12050610. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and Outcomes of Achromobacter Species Infections in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis: a North American Cohort Study.J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Jul;55(7):2074-2085. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02556-16. Epub 2017 Apr 26. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28446570 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Phage Therapy against Pandrug-Resistant Achromobacter xylosoxidans in a 12-Year-Old Lung-Transplanted Cystic Fibrosis Patient.Viruses. 2021 Jan 5;13(1):60. doi: 10.3390/v13010060. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33466377 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of Achromobacter Species in 12 French Cystic Fibrosis Centers in 2020 by a Retrospective MALDI-TOF MS Spectrum Analysis.J Clin Microbiol. 2022 Jun 15;60(6):e0242221. doi: 10.1128/jcm.02422-21. Epub 2022 May 5. J Clin Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35510500 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of Achromobacter xylosoxidans Airway Infection with Disease Severity in Cystic Fibrosis.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 3;14(7):2437. doi: 10.3390/jcm14072437. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40217889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amoureux L, Bador J, Fardeheb S, Mabille C, Couchot C, Massip C, et al. Detection of Achromobacter xylosoxidans in hospital, domestic, and outdoor environmental samples and comparison with human clinical isolates. Appl Environm Microbiol. 2013;79:7142–9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02293-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

