Prognostic role of sentinel lymph node biopsy for patients with cutaneous melanoma: A retrospective study of surveillance, epidemiology, and end-result population-based data
- PMID: 27344178
- PMCID: PMC5216751
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10140
Prognostic role of sentinel lymph node biopsy for patients with cutaneous melanoma: A retrospective study of surveillance, epidemiology, and end-result population-based data
Abstract
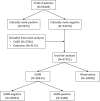
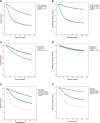
Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) is a sensitive operation for finding micro-metastasis in patients with cutaneous melanoma without evidence of clinically positive lymph node findings. However, until now, no clinical trials or retrospective studies with large samples have been performed to investigate the clinical role of SLNB for cutaneous melanoma patients. In this study, we used the data of cutaneous melanoma from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database to compare overall survival (OS) and melanoma-specific survival (MSS) outcomes with clinical lymph node and SLN status. In total, 56,285 eligible patients were identified in this study. Cutaneous melanoma patients with clinically-positive lymph nodes had significantly shorter OS (46.1% vs 78.6%, p = 0.000) and MSS (55.8% vs 90.5, p = 0.000) compared with clinically-negative lymph node patients. Patients who underwent SLNB had significantly longer 5-year rates for OS (84.3% vs 70.1, p = 0.000) and MSS (91.5% vs 90.3, p = 0.000) compared with patients who did not undergo SLNB (lymph node observation). Patients with a negative SLNB had a significantly longer 5-year rate for OS (86.5% vs 68.1% vs 46.1, p = 0.000) and MSS (93.7% vs 75.1% 55.8%, p = 0.000) than patients who were SLNB-positive or had clinically-positive lymph nodes. This present study showed that the status of SLN is a valuable prognostic factor in patients with Breslow thickness greater than 1 mm in clinically-negative lymph node cutaneous melanoma.
Keywords: SEER; SLNB; melanoma; survival analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Morton DL, Thompson JF, Cochran AJ, Mozzillo N, Nieweg OE, Roses DF, Hoekstra HJ, Karakousis CP, Puleo CA, Coventry BJ, Kashani-Sabet M, Smithers BM, Paul E, et al. Group M: Final trial report of sentinel-node biopsy versus nodal observation in melanoma. The New England journal of medicine. 2014;370:599–609. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morton DL, Thompson JF, Cochran AJ, Mozzillo N, Elashoff R, Essner R, Nieweg OE, Roses DF, Hoekstra HJ, Karakousis CP, Reintgen DS, Coventry BJ, Glass EC, et al. Group M: Sentinel-node biopsy or nodal observation in melanoma. The New England journal of medicine. 2006;355:1307–1317. - PubMed
-
- Morton DL, Wen DR, Wong JH, Economou JS, Cagle LA, Storm FK, Foshag LJ, Cochran AJ. Technical details of intraoperative lymphatic mapping for early stage melanoma. Archives of surgery. 1992;127:392–399. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

