KRT19 directly interacts with β-catenin/RAC1 complex to regulate NUMB-dependent NOTCH signaling pathway and breast cancer properties
- PMID: 27345400
- PMCID: PMC5270332
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2016.221
KRT19 directly interacts with β-catenin/RAC1 complex to regulate NUMB-dependent NOTCH signaling pathway and breast cancer properties
Abstract
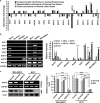
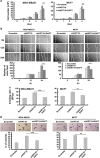
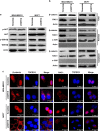
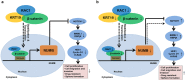
Studies have reported that interactions between keratins (KRTs) and other proteins initiate signaling cascades that regulate cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. In the current study, we found that expression of KRT19 was specifically high in breast cancers and significantly correlated with their invasiveness. Moreover, knockdown of KRT19 led to increased proliferation, migration, invasion, drug resistance, and sphere formation in breast cancer cells via an upregulated NOTCH signaling pathway. This was owing to reduced expression of NUMB, an inhibitory protein of the NOTCH signaling pathway. In addition, we found that KRT19 interacts with β-catenin/RAC1 complex and enhances the nuclear translocation of β-catenin. Concordantly, knockdown of KRT19 suppressed the nuclear translocation of β-catenin as well as β-catenin-mediated NUMB expression. Furthermore, modulation of KRT19-mediated regulation of NUMB and NOTCH1 expression led to the repression of the cancer stem cell properties of breast cancer patient-derived CD133high/CXCR4high/ALDH1high cancer stem-like cells (CSLCs), which showed very low KRT19 and high NOTCH1 expression. Taken together, our study suggests a novel function for KRT19 in the regulation of nuclear import of the β-catenin/RAC1 complex, thus modulating the NUMB-dependent NOTCH signaling pathway in breast cancers and CSLCs, which might bear potential clinical implications for cancer or CSLC treatment.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Cytokeratin 19 (KRT19) has a Role in the Reprogramming of Cancer Stem Cell-Like Cells to Less Aggressive and More Drug-Sensitive Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 9;19(5):1423. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051423. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29747452 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing Regulation of Cancer Properties via KRT19-Mediated Differential Modulation of Wnt/β-Catenin/Notch Signaling in Breast and Colon Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jan 15;11(1):99. doi: 10.3390/cancers11010099. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30650643 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cell proliferation and migration by keratin19-induced nuclear import of early growth response-1 in breast cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Aug 15;19(16):4335-46. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3295. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23833298
-
The role of NUMB/NUMB isoforms in cancer stem cells.BMB Rep. 2021 Jul;54(7):335-343. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2021.54.7.048. BMB Rep. 2021. PMID: 34078527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of angiogenesis via Notch signaling in breast cancer and cancer stem cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1836(2):304-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2013.10.003. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24183943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and prognostic analysis of biomarkers to predict the progression of pancreatic cancer patients.Mol Med. 2022 Apr 15;28(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00467-8. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35428170 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokeratin 19 (KRT19) has a Role in the Reprogramming of Cancer Stem Cell-Like Cells to Less Aggressive and More Drug-Sensitive Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 9;19(5):1423. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051423. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29747452 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of cancer-associated fibroblasts-related gene landscape in prognosis and immune microenvironment of bladder cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 15;13:1174252. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1174252. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37397364 Free PMC article.
-
Size matters: Biomolecular compositions of small and large extracellular vesicles in the urine of glioblastoma patients.J Extracell Biol. 2024 Nov 15;3(11):e70021. doi: 10.1002/jex2.70021. eCollection 2024 Nov. J Extracell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39554867 Free PMC article.
-
Signs of carcinogenicity induced by parathion, malathion, and estrogen in human breast epithelial cells (Review).Oncol Rep. 2021 Apr;45(4):24. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.7975. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33649804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ignatiadis M, Xenidis N, Perraki M, Apostolaki S, Politaki E, Kafousi M et al. Different prognostic value of cytokeratin-19 mrna–positive circulating tumor cells according to estrogen receptor and HER2 status in early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 5194–5202. - PubMed
-
- Bozionellou V, Mavroudis D, Perraki M, Papadopoulos S, Apostolaki S, Stathopoulos E et al. Trastuzumab administration can effectively target chemotherapy-resistant cytokeratin-19 messenger RNA–positive tumor cells in the peripheral blood and bone marrow of patients with breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 8185–8194. - PubMed
-
- Coulombe PA, Wong P. Cytoplasmic intermediate filaments revealed as dynamic and multipurpose scaffolds. Nat Cell Biol 2004; 6: 699–706. - PubMed
-
- Omary MB, Ku N-O, Tao G-Z, Toivola DM, Liao J. ‘Heads and tails' of intermediate filament phosphorylation: multiple sites and functional insights. Trends Biochem Sci 2006; 31: 383–394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

