Contrasting the Genetic Architecture of 30 Complex Traits from Summary Association Data
- PMID: 27346688
- PMCID: PMC5005444
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.05.013
Contrasting the Genetic Architecture of 30 Complex Traits from Summary Association Data
Abstract
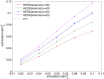
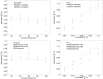
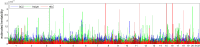
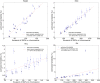
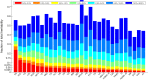
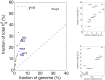
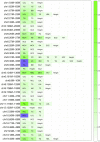
Variance-component methods that estimate the aggregate contribution of large sets of variants to the heritability of complex traits have yielded important insights into the genetic architecture of common diseases. Here, we introduce methods that estimate the total trait variance explained by the typed variants at a single locus in the genome (local SNP heritability) from genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary data while accounting for linkage disequilibrium among variants. We applied our estimator to ultra-large-scale GWAS summary data of 30 common traits and diseases to gain insights into their local genetic architecture. First, we found that common SNPs have a high contribution to the heritability of all studied traits. Second, we identified traits for which the majority of the SNP heritability can be confined to a small percentage of the genome. Third, we identified GWAS risk loci where the entire locus explains significantly more variance in the trait than the GWAS reported variants. Finally, we identified loci that explain a significant amount of heritability across multiple traits.
Copyright © 2016 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Locke A.E., Kahali B., Berndt S.I., Justice A.E., Pers T.H., Day F.R., Powell C., Vedantam S., Buchkovich M.L., Yang J., LifeLines Cohort Study. ADIPOGen Consortium. AGEN-BMI Working Group. CARDIOGRAMplusC4D Consortium. CKDGen Consortium. GLGC. ICBP. MAGIC Investigators. MuTHER Consortium. MIGen Consortium. PAGE Consortium. ReproGen Consortium. GENIE Consortium. International Endogene Consortium Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature. 2015;518:197–206. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wood A.R., Esko T., Yang J., Vedantam S., Pers T.H., Gustafsson S., Chu A.Y., Estrada K., Luan J., Kutalik Z., Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMEMERGEGE) Consortium. MIGen Consortium. PAGEGE Consortium. LifeLines Cohort Study Defining the role of common variation in the genomic and biological architecture of adult human height. Nat. Genet. 2014;46:1173–1186. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

