Innate sensing of oxidation-specific epitopes in health and disease
- PMID: 27346802
- PMCID: PMC7097710
- DOI: 10.1038/nri.2016.63
Innate sensing of oxidation-specific epitopes in health and disease
Abstract
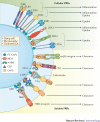
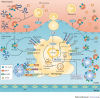
Ageing, infections and inflammation result in oxidative stress that can irreversibly damage cellular structures. The oxidative damage of lipids in membranes or lipoproteins is one of these deleterious consequences that not only alters lipid function but also leads to the formation of neo-self epitopes - oxidation-specific epitopes (OSEs) - which are present on dying cells and damaged proteins. OSEs represent endogenous damage-associated molecular patterns that are recognized by pattern recognition receptors and the proteins of the innate immune system, and thereby enable the host to sense and remove dangerous biological waste and to maintain homeostasis. If this system is dysfunctional or overwhelmed, the accumulation of OSEs can trigger chronic inflammation and the development of diseases, such as atherosclerosis and age-related macular degeneration. Understanding the molecular components and mechanisms that are involved in this process will help to identify individuals with an increased risk of developing chronic inflammation, and will also help to indicate novel modes of therapeutic intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
J.L.W. is an inventor and receives royalties from patents or patent applications owned by the University of California San Diego, USA, on oxidation-specific antibodies.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

