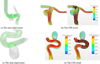Rapid Virtual Stenting for Intracranial Aneurysms
- PMID: 27346910
- PMCID: PMC4917288
- DOI: 10.1117/12.2216123
Rapid Virtual Stenting for Intracranial Aneurysms
Abstract
The rupture of Intracranial Aneurysms is the most severe form of stroke with high rates of mortality and disability. One of its primary treatments is to use stent or Flow Diverter to divert the blood flow away from the IA in a minimal invasive manner. To optimize such treatments, it is desirable to provide an automatic tool for virtual stenting before its actual implantation. In this paper, we propose a novel method, called ball-sweeping, for rapid virtual stenting. Our method sweeps a maximum inscribed sphere through the aneurysmal region of the vessel and directly generates a stent surface touching the vessel wall without needing to iteratively grow a deformable stent surface. Our resulting stent mesh has guaranteed smoothness and variable pore density to achieve an enhanced occlusion performance. Comparing to existing methods, our technique is computationally much more efficient.
Figures
References
-
- Antiga L, et al. VMTK: Vascular Modeling Toolkit. http://www.vmtk.org.
-
- Berg M, Cheong O, Kreveld M, Overmars M. Computational Geometry: Algorithms and Applications. Springer; 2008.
-
- Cebral JR, Lohner R. Efficient simulation of blood flow past complex endovascular devices using an adaptive embedding technique. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2005;24(4) - PubMed
-
- Delingette H. General Object Reconstruction Based on Simplex Meshes. International Journal of Computer Vision. 1999;32(2)
-
- Dijkstra EW. A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numerische Mathematik. 1
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources