Experimental study of USPIO-enhanced MRI in the detection of atherosclerotic plaque and the intervention of atorvastatin
- PMID: 27347029
- PMCID: PMC4907054
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3266
Experimental study of USPIO-enhanced MRI in the detection of atherosclerotic plaque and the intervention of atorvastatin
Abstract
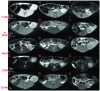
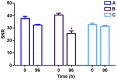
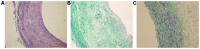
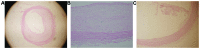
Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide (USPIO) can identify atherosclerotic vulnerable plaque and atorvastatin can stabilize vulnerable plaque by inhibiting the inflammatory response. Using balloon injury in rabbit abdominal aortic endothelial cells and p53 gene transfecting the local plaque, we established an atherosclerotic vulnerable plaque model. In the treatment group, animals were treated with atorvastatin for 8 weeks. At the end of week 16, the animals in each group underwent medication trigger. USPIO-enhanced MRI was utilized to detect vulnerable plaque formation and the transformation of stable plaque in the treatment group. Pathological and serological studies were conducted in animal sera and tissues. The images from the USPIO-enhanced MRI, and the vulnerable plaque showed low signal, especially on T2*-weighted sequences (T2*WI). Plaque signal strength reached a negative enhancement peak at 96 h. Compared with the other groups, lipids, cell adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 levels were significantly lower (P<0.05) in the treatment group. In conclusion, USPIO-enhanced MRI can identify vulnerable plaque formation by deposition in macrophages, while atorvastatin is able to inhibit the progression of atherosclerosis and promote plaque transformation to the stable form.
Keywords: atherosclerotic plaque; cell adhesion molecule-1; superparamagnetic iron oxide.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of Vulnerable Atherosclerotic Plaques in Experimental Atherosclerosis with the USPIO-Enhanced MRI.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015 Nov;73(2):331-337. doi: 10.1007/s12013-015-0591-y. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 27352319
-
Identifying Vulnerable Atherosclerotic Plaque in Rabbits Using DMSA-USPIO Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Investigate the Effect of Atorvastatin.PLoS One. 2015 May 14;10(5):e0125677. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125677. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25973795 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin inhibits macrophage infiltration and promotes plaque stabilization by upregulating anti-inflammatory HGF/c-Met system in the atherosclerotic rabbit: USPIO-enhanced MRI assessment.Vascul Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;127:106659. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2020.106659. Epub 2020 Feb 15. Vascul Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32068091
-
Macrophage imaging in central nervous system and in carotid atherosclerotic plaque using ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide in magnetic resonance imaging.Invest Radiol. 2004 Oct;39(10):619-25. doi: 10.1097/01.rli.0000135980.08491.33. Invest Radiol. 2004. PMID: 15377941 Review.
-
[Iron-oxide-enhanced MR imaging of inflammatory atherosclerotic lesions: overview of experimental and initial clinical results].Rofo. 2003 Apr;175(4):469-76. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-38434. Rofo. 2003. PMID: 12677500 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Molecular Imaging of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 in Atherosclerosis Using a Smart Multifunctional PET/MRI Nanoparticle.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Dec 28;17:6773-6789. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S385679. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36600879 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6-targeted ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for optimized MRI detection of atherosclerotic vulnerable plaques in rabbits.RSC Adv. 2020 Apr 17;10(26):15346-15353. doi: 10.1039/c9ra10509c. eCollection 2020 Apr 16. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35495447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang HD, Yu SQ, Gao F, Qin ML. The anti-atherosclerosiseffect of adiponectin. Chongqing Med J. 2009;38:2509–2510. (In Chinese)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
