Gamma Knife radiosurgery combined with stereotactic aspiration as an effective treatment method for large cystic brain metastases
- PMID: 27347148
- PMCID: PMC4907086
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.4603
Gamma Knife radiosurgery combined with stereotactic aspiration as an effective treatment method for large cystic brain metastases
Abstract
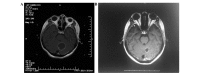
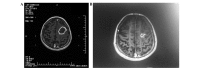
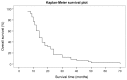
In the present study, the efficacy and clinical outcomes of stereotactic aspiration combined with the Gamma Knife radiosurgery (GKRS) method were evaluated retrospectively for patients with large cystic brain metastases. This combined method aims to decrease the tumor weight (volume) and increase the possible radiation dose. The present study involved 48 patients who were diagnosed with cystic metastatic brain tumors between January 2008 and December 2012 in the Department of Neurosurgery of Nanfang Hospital Southern Medical University (Guangzhou, China). Every patient underwent Leksell stereotactic frame, 1.5T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-guided stereotactic cyst aspiration and Leksell GKRS. Subsequent to the therapy, MRI was performed every 3 months. The results indicated that 48 cases were followed up for 24-72 months, with a mean follow-up duration of 36.2 months. Following treatment, 44 patients (91.7%) exhibited tumor control and 4 patients (8.3%) experienced progression of the local tumor. During this period, 35 patients (72.9%) succumbed, but only 2 (4.2%) of these succumbed to the brain metastases. The total local control rate was 91.7% and the median overall survival time of all patients was 19.5 months. The 1-year overall survival rate was 70.8% and the 2-year overall survival rate was 26.2%. In conclusion, these results indicated that the method of stereotactic cyst aspiration combined with GKRS was safe and effective for patients with large cystic brain metastases. This method is effective for patients whose condition is too weak for general anesthesia and in whom the tumors are positioned at eloquent areas. This method enables patients to avoid a craniotomy, and provides a good tumor control rate, survival time and quality of life.
Keywords: Gamma Knife radiosurgery; colloidal phosphorus-32; cystic brain metastases; stereotactic cyst aspiration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gamma knife radiosurgery after stereotactic aspiration for large cystic brain metastases.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009 Oct;46(4):360-4. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2009.46.4.360. Epub 2009 Oct 31. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009. PMID: 19893727 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic cyst aspiration directly followed by Gamma Knife radiosurgery for large cystic brain metastases.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021 Feb;163(2):343-350. doi: 10.1007/s00701-020-04273-1. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021. PMID: 32291592
-
Fractionated Gamma Knife radiosurgery after cyst aspiration for large cystic brain metastases: case series and literature review.Neurosurg Rev. 2022 Oct;45(5):3457-3465. doi: 10.1007/s10143-022-01835-y. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Neurosurg Rev. 2022. PMID: 35834076 Review.
-
Alternative treatment of stereotactic cyst aspiration and radiosurgery for cystic brain metastases.Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2014;92(4):234-41. doi: 10.1159/000362935. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 25138737 Clinical Trial.
-
Stereotactic aspiration alone or Ommaya placement and aspiration followed by stereotactic radiosurgery for cystic brain metastasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Brain Spine. 2025 Jan 11;5:104184. doi: 10.1016/j.bas.2025.104184. eCollection 2025. Brain Spine. 2025. PMID: 39935528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cystic brain metastases had slower speed of tumor shrinkage but similar prognosis compared with solid tumors that underwent radiosurgery treatment.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Feb 20;11:1753-1763. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S188674. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 30858728 Free PMC article.
-
Local control after brain-directed radiation in patients with cystic versus solid brain metastases.J Neurooncol. 2019 Apr;142(2):355-363. doi: 10.1007/s11060-019-03106-1. Epub 2019 Feb 4. J Neurooncol. 2019. PMID: 30715665
-
Cystic brain metastases in ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer.Ecancermedicalscience. 2018 Mar 14;12:818. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2018.818. eCollection 2018. Ecancermedicalscience. 2018. PMID: 29662531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Radiotherapy Efficacy and Prognostic Analysis for Solid and Cystic Brain Metastases.Cancer Control. 2024 Jan-Dec;31:10732748241266476. doi: 10.1177/10732748241266476. Cancer Control. 2024. PMID: 39030537 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal treatment paradigm for unstaged resection of a large cystic brain metastasis: illustrative case.J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024 Nov 25;8(22):CASE24357. doi: 10.3171/CASE24357. Print 2024 Nov 25. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2024. PMID: 39586082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, Werner-Wasik M, Demas W, Ryu J, Bahary JP, et al. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: Phase III results of the RTGO 9508 randomized trial. Lancet. 2004;363:1665–1672. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16250-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsao MN, Lioyd N, Wong R, Chow E, Rakovitch E, Laperriere N. Whole brain radiotherapy for the treatment of multiple brain metastases. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;4:CD003869. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, Kenjyo M, Oya N, Hirota S, Shioura H, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs. stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295:2483–2491. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.21.2483. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
