Expression of Prostatic Acid Phosphatase in Rat Circumvallate Papillae
- PMID: 27348306
- PMCID: PMC4922667
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158401
Expression of Prostatic Acid Phosphatase in Rat Circumvallate Papillae
Abstract
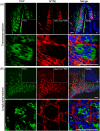
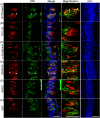
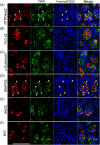
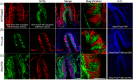
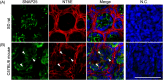
ATP and its metabolites are important for taste signaling in taste buds, and thus a clearance system for them would play critical roles in maintenance of gustatory function. A previous report revealed that mRNAs for ecto-5'-nucleotidase (NT5E) and prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) were expressed by taste cells of taste buds, and NT5E-immunoreactivity was detected in taste cells. However, there was no information on PAP-immunoreactivity in taste buds. In this study, we examined the expression profile of PAP in rat taste buds. In the isolated rat taste buds, we detected expression of mRNA for PAP, but NT5E was not detected differing from the case of mouse ones (Dando et al., 2012, J Neuroscience). On immunohistochemical analysis, PAP-immunoreactivity was found predominantly in NTPDase2-positive type I and SNAP25-positive type III taste cells, while there were no apparent signals of it in PLC-β2-positive type II, α-gustducin-positive type II, AADC-positive type III and 5HT-positive type III ones. As for NT5E, we could not detect its immunoreactivity in rat taste buds, and co-localization of it with any taste cell markers, although mouse taste buds expressed NT5E as reported previously. These findings suggest that PAP expressed by type I and one of type III taste cells of rats may contribute to metabolic regulation of the extracellular levels of adenine nucleotides in the taste buds of circumvallate papillae, and the regulating mechanisms for adenine nucleotides in taste buds might be different between rats and mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 in rat circumvallate papillae.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Jan 15;533:104-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.10.063. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 23147119
-
Immunohistochemical localization of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase in mouse taste buds and developing taste papillae.Histochem Cell Biol. 2007 Apr;127(4):415-22. doi: 10.1007/s00418-006-0257-3. Epub 2007 Jan 9. Histochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17211625
-
Patterns of immunoreactivity specific for gustducin and for NCAM differ in developing rat circumvallate papillae and their taste buds.Acta Histochem. 2012 May;114(3):259-69. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2011.06.001. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Acta Histochem. 2012. PMID: 21703667
-
Expression of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors in rat gustatory papillae.Cell Tissue Res. 2007 Apr;328(1):57-63. doi: 10.1007/s00441-006-0351-9. Epub 2007 Jan 10. Cell Tissue Res. 2007. PMID: 17216195
-
Expression of alpha-gustducin in the circumvallate papillae of taste buds of diabetic rats.Acta Histochem. 2009;111(2):145-9. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2008.05.007. Epub 2008 Sep 27. Acta Histochem. 2009. PMID: 18824257
Cited by
-
Novel, Fully Characterised Bovine Taste Bud Cells of Fungiform Papillae.Cells. 2021 Sep 2;10(9):2285. doi: 10.3390/cells10092285. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Finger TE, Danilova V, Barrows J, Bartel DL, Vigers AJ, Stone L, et al. ATP signaling is crucial for communication from taste buds to gustatory nerves. Science. 2005;310(5753):1495–9. . - PubMed
-
- Kataoka S, Toyono T, Seta Y, Ogura T, Toyoshima K. Expression of P2Y1 receptors in rat taste buds. Histochemistry and cell biology. 2004;121(5):419–26. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

