Temperature-Responsive Smart Nanocarriers for Delivery Of Therapeutic Agents: Applications and Recent Advances
- PMID: 27349465
- PMCID: PMC5003094
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b00371
Temperature-Responsive Smart Nanocarriers for Delivery Of Therapeutic Agents: Applications and Recent Advances
Abstract
Smart drug delivery systems (DDSs) have attracted the attention of many scientists, as carriers that can be stimulated by changes in environmental parameters such as temperature, pH, light, electromagnetic fields, mechanical forces, etc. These smart nanocarriers can release their cargo on demand when their target is reached and the stimulus is applied. Using the techniques of nanotechnology, these nanocarriers can be tailored to be target-specific, and exhibit delayed or controlled release of drugs. Temperature-responsive nanocarriers are one of most important groups of smart nanoparticles (NPs) that have been investigated during the past decades. Temperature can either act as an external stimulus when heat is applied from the outside, or can be internal when pathological lesions have a naturally elevated termperature. A low critical solution temperature (LCST) is a special feature of some polymeric materials, and most of the temperature-responsive nanocarriers have been designed based on this feature. In this review, we attempt to summarize recent efforts to prepare innovative temperature-responsive nanocarriers and discuss their novel applications.
Keywords: LCST/UCST behavior; anticancer delivery; characterization; dual/multi responsive; gene delivery; smart drug delivery systems; synthesis; temperature-responsive nanocarriers.
Conflict of interest statement
Notes The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




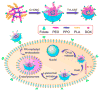

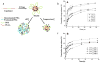


References
-
- Wang C, Xu H, Liang C, Liu Y, Li Z, Yang G, Cheng L, Li Y, Liu Z. Iron Oxide@ Polypyrrole Nanoparticles As A Multifunctional Drug Carrier For Remotely Controlled Cancer Therapy With Synergistic Antitumor Effect. ACS Nano. 2013;7(8):6782–6795. - PubMed
-
- Sahoo B, Devi KSP, Banerjee R, Maiti TK, Pramanik P, Dhara D. Thermal And pH Responsive Polymer-Tethered Multifunctional Magnetic Nanoparticles For Targeted Delivery Of Anticancer Drug. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(9):3884–3893. - PubMed
-
- De Smet M, Langereis S, Van Den Bosch S, Bitter K, Hijnen NM, Heijman E, Grüll H. SPECT/CT Imaging Of Temperature-Sensitive Liposomes For MR-Image Guided Drug Delivery With High Intensity Focused Ultrasound. J Controlled Release. 2013;169(1):82–90. - PubMed
-
- Wang AZ, Langer R, Farokhzad OC. Nanoparticle Delivery Of Cancer Drugs. Annu Rev Med. 2012;63:185–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

