Efficacy and safety of palbociclib in combination with letrozole as first-line treatment of ER-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer: expanded analyses of subgroups from the randomized pivotal trial PALOMA-1/TRIO-18
- PMID: 27349747
- PMCID: PMC4924326
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-016-0721-5
Efficacy and safety of palbociclib in combination with letrozole as first-line treatment of ER-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer: expanded analyses of subgroups from the randomized pivotal trial PALOMA-1/TRIO-18
Abstract
Background: Palbociclib is an oral small-molecule inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6. In the randomized, open-label, phase II PALOMA-1/TRIO-18 trial, palbociclib in combination with letrozole improved progression-free survival (PFS) compared with letrozole alone as first-line treatment of estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative, advanced breast cancer (20.2 months versus 10.2 months; hazard ratio (HR) = 0.488, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.319-0.748; one-sided p = 0.0004). Grade 3-4 neutropenia was the most common adverse event (AE) in the palbociclib + letrozole arm. We now present efficacy and safety analyses based on several specific patient and tumor characteristics, and present in detail the clinical patterns of neutropenia observed in the palbociclib + letrozole arm of the overall safety population.
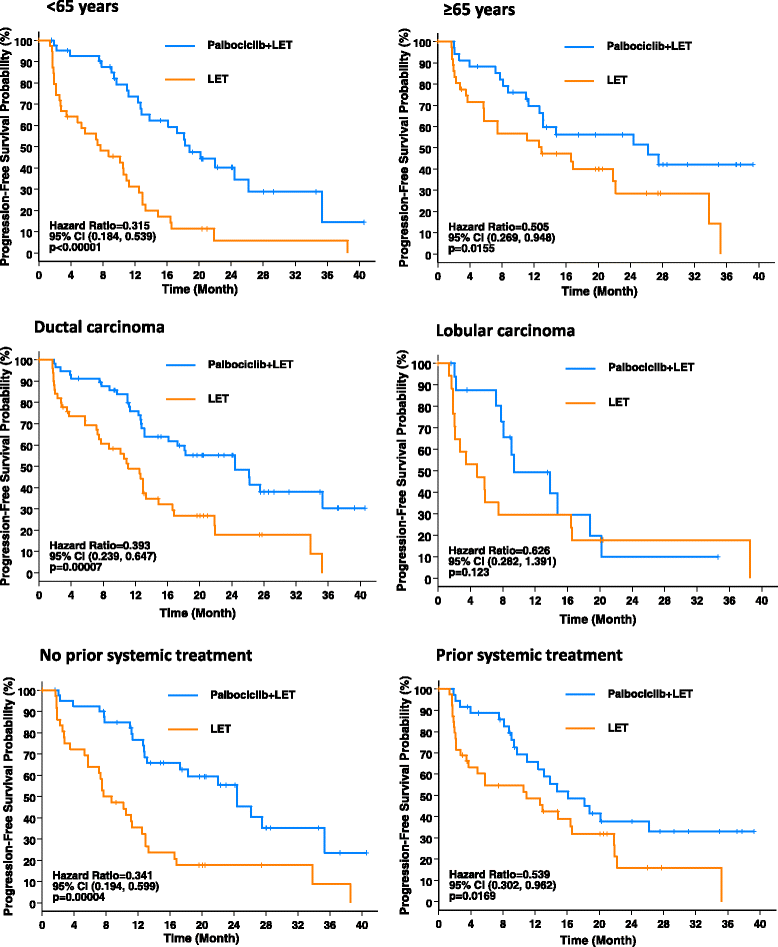
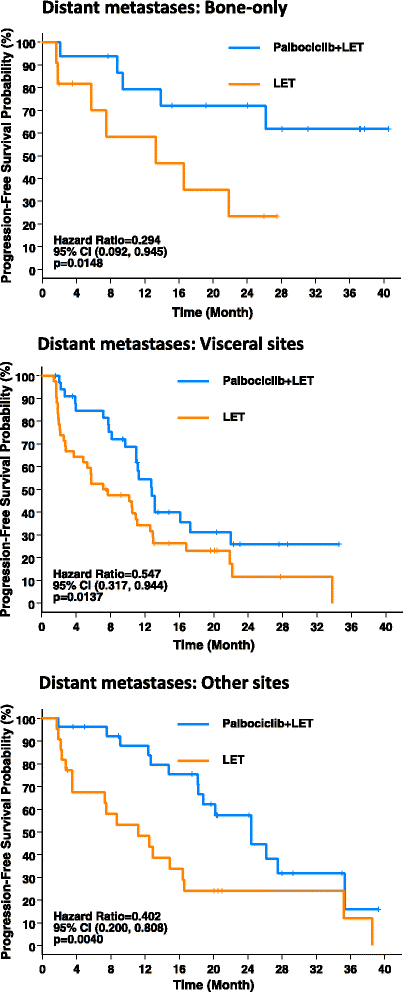
Methods: Postmenopausal women (n = 165) with ER+, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer who had not received any systemic treatment for their advanced disease were randomized 1:1 to receive either palbociclib in combination with letrozole or letrozole alone. Treatment continued until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, consent withdrawal, or death. The primary endpoint was PFS. We now analyze the difference in PFS for the treatment populations by subgroups, including age, histological type, history of prior neoadjuvant/adjuvant systemic treatment, and sites of distant metastasis, using the Kaplan-Meier method. HR and 95 % CI are derived from a Cox proportional hazards regression model.
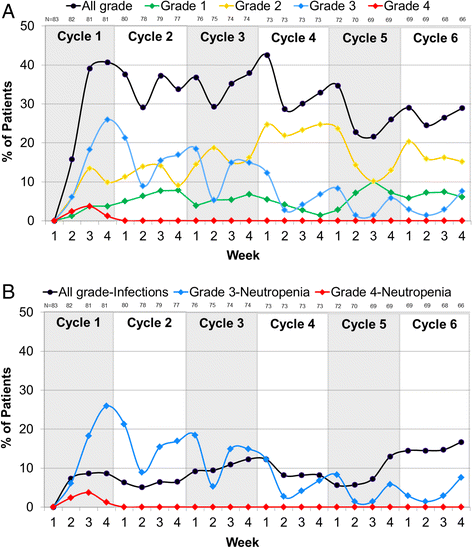
Results: A clinically meaningful improvement in median PFS and clinical benefit response (CBR) rate was seen with palbociclib + letrozole in every subgroup evaluated. Grade 3-4 neutropenia was the most common AE with palbociclib + letrozole in all subgroups. Analysis of the frequency of neutropenia by grade during the first six cycles of treatment showed that there was a downward trend in Grade 3-4 neutropenia over time. Among those who experienced Grade 3-4 neutropenia, 71.7 % had no overlapping infections of any grade and none had overlapping Grade 3-4 infections.
Conclusion: The magnitude of clinical benefit seen with the addition of palbociclib to letrozole in improving both median PFS and CBR rate is consistent in nearly all subgroups analyzed, and consistent with that seen in the overall study population. The safety profile of the combination treatment in all subgroups was also comparable to that in the overall safety population of the study.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cyclin-dependent kinase; Estrogen receptor-positive; HER2-negative; Neutropenia.
Figures
References
-
- Fry DW, Harvey PJ, Keller PR, Elliott WL, Meade M, Trachet E, et al. Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by PD 0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004;3(11):1427–38. - PubMed
-
- Finn RS, Dering J, Conklin D, Kalous O, Cohen DJ, Desai AJ, et al. PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):R77. doi: 10.1186/bcr2419. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Finn RS, Crown JP, Lang I, Boer K, Bondarenko IM, Kulyk SO, et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): a randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71159-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- DeMichele A, Clark AS, Tan KS, Heitjan DF, Gramlich K, Gallagher M, et al. CDK 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib (PD0332991) in Rb + advanced breast cancer: phase ii activity, safety, and predictive biomarker assessment. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(5):995–1001. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2258. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

