Radioresistance of GGG sequences to prompt strand break formation from direct-type radiation damage
- PMID: 27349757
- PMCID: PMC5093048
- DOI: 10.1007/s00411-016-0660-7
Radioresistance of GGG sequences to prompt strand break formation from direct-type radiation damage
Abstract
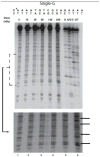
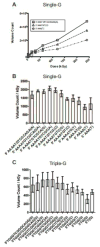
As humans, we are constantly exposed to ionizing radiation from natural, man-made and cosmic sources which can damage DNA, leading to deleterious effects including cancer incidence. In this work, we introduce a method to monitor strand breaks resulting from damage due to the direct effect of ionizing radiation and provide evidence for sequence-dependent effects leading to strand breaks. To analyze only DNA strand breaks caused by radiation damage due to the direct effect of ionizing radiation, we combined an established technique to generate dehydrated DNA samples with a technique to analyze single-strand breaks on short oligonucleotide sequences via denaturing gel electrophoresis. We find that direct damage primarily results in a reduced number of strand breaks in guanine triplet regions (GGG) when compared to isolated guanine (G) bases with identical flanking base context. In addition, we observe strand break behavior possibly indicative of protection of guanine bases when flanked by pyrimidines and sensitization of guanine to strand break when flanked by adenine (A) bases in both isolated G and GGG cases. These observations provide insight into the strand break behavior in GGG regions damaged via the direct effect of ionizing radiation. In addition, this could be indicative of DNA sequences that are naturally more susceptible to strand break due to the direct effect of ionizing radiation.
Keywords: DNA damage; Direct effect; Gel electrophoresis; Guanine; Ionizing radiation; Radiation chemistry; Radiosensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
Author ASM declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author PJB declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author JJH declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Figures
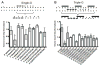
Similar articles
-
8-OxoG retards the activity of the ligase III/XRCC1 complex during the repair of a single-strand break, when present within a clustered DNA damage site.DNA Repair (Amst). 2004 Mar 4;3(3):289-99. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2003.11.006. DNA Repair (Amst). 2004. PMID: 15177044
-
Modelling the effect of incorporated halogenated pyrimidine on radiation-induced DNA strand breaks.Int J Radiat Biol. 2002 Nov;78(11):953-66. doi: 10.1080/0955300021000024270. Int J Radiat Biol. 2002. PMID: 12456283
-
Correlation of free radical yields with strand break yields produced in plasmid DNA by the direct effect of ionizing radiation.J Phys Chem B. 2005 Sep 8;109(35):16967-73. doi: 10.1021/jp0518409. J Phys Chem B. 2005. PMID: 16853159 Free PMC article.
-
The role of DNA single- and double-strand breaks in cell killing by ionizing radiation.Radiat Res. 1998 Nov;150(5 Suppl):S42-51. Radiat Res. 1998. PMID: 9806608 Review.
-
Genetic variations in DNA repair genes, radiosensitivity to cancer and susceptibility to acute tissue reactions in radiotherapy-treated cancer patients.Acta Oncol. 2008;47(5):809-24. doi: 10.1080/02841860801885969. Acta Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18568480 Review.
References
-
- Arumainayagam CR, Lee HL, Nelson RB, Haines DR, Gunawardane RP. Low energy electron-induced reactions in condensed matter. Surf Sci Rep. 2010;65:1–44. doi: 10.1016/j.surfrep.2009.09.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

