Controlled release of NELL-1 protein from chitosan/hydroxyapatite-modified TCP particles
- PMID: 27349789
- PMCID: PMC6705139
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.06.050
Controlled release of NELL-1 protein from chitosan/hydroxyapatite-modified TCP particles
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Controlled release of NELL-1 protein from chitosan/hydroxyapatite-modified TCP particles" [Int. J. Pharmaceut. 511(1) (2016) 79-89].Int J Pharm. 2020 Jan 25;574:118938. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118938. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31864672 No abstract available.
Abstract
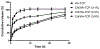
NEL-like molecule-1 (NELL-1) is a novel osteogenic protein that showing high specificity to osteochondral cells. It was widely used in bone regeneration research by loading onto carriers such as tricalcium phosphate (TCP) particles. However, there has been little research on protein controlled release from this material and its potential application. In this study, TCP was first modified with a hydroxyapatite coating followed by a chitosan coating to prepare chitosan/hydroxyapatite-coated TCP particles (Chi/HA-TCP). The preparation was characterized by SEM, EDX, FTIR, XRD, FM and Zeta potential measurements. The NELL-1 loaded Chi/HA-TCP particles and the release kinetics were investigated in vitro. It was observed that the Chi/HA-TCP particles prepared with the 0.3% (wt/wt) chitosan solution were able to successfully control the release of NELL-1 and maintain a slow, steady release for up to 28 days. Furthermore, more than 78% of the loaded protein's bioactivity was preserved in Chi/HA-TCP particles over the period of the investigation, which was significantly higher than that of the protein released from hydroxyapatite coated TCP (HA-TCP) particles. Collectively, this study suggests that the osteogenic protein NELL-1 showed a sustained release pattern after being encapsulated into the modified Chi/HA-TCP particles, and the NELL-1 integrated composite of Chi/HA-TCP showed a potential to function as a protein delivery carrier and as an improved bone matrix for use in bone regeneration research.
Keywords: Bioactivity; Chitosan; Hydroxyapatite; NELL-1; Release kinetics; TCP.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Drs. Wu, Ting, Soo, and Zhang are co-founders of Bone Biologics, Inc., which sublicenses NELL-1 related patents from the UC Regents.
Figures








References
-
- Abarrategi A, Moreno-Vicente C, Ramos V, Aranaz I, Sanz Casado JV, López-Lacomba JL, 2008. Improvement of porous β-TCP scaffolds with rhBMP-2 chitosan carrier film for bone tissue application. Tissue Engineering Part A 14, 1305–1319. - PubMed
-
- Arner JW, Santrock RD, 2014. A historical review of common bone graft materials in foot and ankle surgery. Foot & ankle specialist 7, 143–151. - PubMed
-
- Babiker H, 2013. Bone graft materials in fixation of orthopaedic implants in sheep. Danish medical journal 60, B4680. - PubMed
-
- Bauer TW, Muschler GF, 2000. Bone graft materials. An overview of the basic science. Clinical orthopaedics and related research, 10–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

