Crystal structure of a PP2A B56-BubR1 complex and its implications for PP2A substrate recruitment and localization
- PMID: 27350047
- PMCID: PMC4930772
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-016-0283-4
Crystal structure of a PP2A B56-BubR1 complex and its implications for PP2A substrate recruitment and localization
Abstract
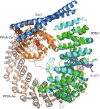
Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) accounts for the majority of total Ser/Thr phosphatase activities in most cell types and regulates many biological processes. PP2A holoenzymes contain a scaffold A subunit, a catalytic C subunit, and one of the regulatory/targeting B subunits. How the B subunit controls PP2A localization and substrate specificity, which is a crucial aspect of PP2A regulation, remains poorly understood. The kinetochore is a critical site for PP2A functioning, where PP2A orchestrates chromosome segregation through its interactions with BubR1. The PP2A-BubR1 interaction plays important roles in both spindle checkpoint silencing and stable microtubule-kinetochore attachment. Here we present the crystal structure of a PP2A B56-BubR1 complex, which demonstrates that a conserved BubR1 LxxIxE motif binds to the concave side of the B56 pseudo-HEAT repeats. The BubR1 motif binds to a groove formed between B56 HEAT repeats 3 and 4, which is quite distant from the B56 binding surface for PP2A catalytic C subunit and thus is unlikely to affect PP2A activity. In addition, the BubR1 binding site on B56 is far from the B56 binding site of shugoshin, another kinetochore PP2A-binding protein, and thus BubR1 and shugoshin can potentially interact with PP2A-B56 simultaneously. Our structural and biochemical analysis indicates that other proteins with the LxxIxE motif may also bind to the same PP2A B56 surface. Thus, our structure of the PP2A B56-BubR1 complex provides important insights into how the B56 subunit directs the recruitment of PP2A to specific targets.
Keywords: BubR1; PP2A; cellular targeting; kinetochore; substrate recruitment.
Figures




Similar articles
-
BUB-1 targets PP2A:B56 to regulate chromosome congression during meiosis I in C. elegans oocytes.Elife. 2020 Dec 23;9:e65307. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65307. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33355089 Free PMC article.
-
Division of labour between PP2A-B56 isoforms at the centromere and kinetochore.Elife. 2019 Mar 4;8:e42619. doi: 10.7554/eLife.42619. Elife. 2019. PMID: 30829571 Free PMC article.
-
Direct binding between BubR1 and B56-PP2A phosphatase complexes regulate mitotic progression.J Cell Sci. 2013 Mar 1;126(Pt 5):1086-92. doi: 10.1242/jcs.122481. Epub 2013 Jan 23. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23345399
-
Phosphatase regulation in cell division: With emphasis on PP2A-B56.Mol Cells. 2025 Sep;48(9):100255. doi: 10.1016/j.mocell.2025.100255. Epub 2025 Jul 18. Mol Cells. 2025. PMID: 40684918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles of B56 Phosphorylation and Binding Motif in PP2A-B56 Holoenzyme Biological Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 10;25(6):3185. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063185. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542160 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural mechanism for inhibition of PP2A-B56α and oncogenicity by CIP2A.Nat Commun. 2023 Feb 28;14(1):1143. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36693-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36854761 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling to short linear motifs creates versatile PME-1 activities in PP2A holoenzyme demethylation and inhibition.Elife. 2022 Aug 4;11:e79736. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79736. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35924897 Free PMC article.
-
Disease mutations and phosphorylation alter the allosteric pathways involved in autoinhibition of protein phosphatase 2A.J Chem Phys. 2023 Jun 7;158(21):215101. doi: 10.1063/5.0150272. J Chem Phys. 2023. PMID: 37260014 Free PMC article.
-
Dual TORCs driven and B56 orchestrated signaling network guides eukaryotic cell migration.BMB Rep. 2017 Sep;50(9):437-444. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.9.091. BMB Rep. 2017. PMID: 28571594 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structure of the deltaretroviral intasome in complex with the PP2A regulatory subunit B56γ.Nat Commun. 2020 Oct 7;11(1):5043. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18874-y. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33028863 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

