Dietary metabolites and the gut microbiota: an alternative approach to control inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 27350881
- PMCID: PMC4910123
- DOI: 10.1038/cti.2016.29
Dietary metabolites and the gut microbiota: an alternative approach to control inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
Abstract
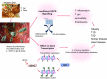
It is now convincingly clear that diet is one of the most influential lifestyle factors contributing to the rise of inflammatory diseases and autoimmunity in both developed and developing countries. In addition, the modern 'Western diet' has changed in recent years with increased caloric intake, and changes in the relative amounts of dietary components, including lower fibre and higher levels of fat and poor quality of carbohydrates. Diet shapes large-bowel microbial ecology, and this may be highly relevant to human diseases, as changes in the gut microbiota composition are associated with many inflammatory diseases. Recent studies have demonstrated a remarkable role for diet, the gut microbiota and their metabolites-the short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)-in the pathogenesis of several inflammatory diseases, such as asthma, arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, colon cancer and wound-healing. This review summarizes how diet, microbiota and gut microbial metabolites (particularly SCFAs) can modulate the progression of inflammatory diseases and autoimmunity, and reveal the molecular mechanisms (metabolite-sensing G protein-coupled receptor (GPCRs) and inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDACs)). Therefore, considerable benefit could be achieved simply through the use of diet, probiotics and metabolites for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory diseases and autoimmunity.
Figures
References
-
- Thorburn AN, Macia L, Mackay CR. Diet, metabolites, and "western-lifestyle" inflammatory diseases. Immunity 2014; 40: 833–842. - PubMed
-
- King DE, Mainous AG 3rd, Lambourne CA. Trends in dietary fiber intake in the United States, 1999-2008. J Acad Nutr Diet 2012; 112: 642–648. - PubMed
-
- Cameron AJ, Welborn TA, Zimmet PZ, Dunstan DW, Owen N, Salmon J et al. Overweight and obesity in Australia: the 1999-2000 Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study (AusDiab). Med J Aust 2003; 178: 427–432. - PubMed
-
- Chow FY, Briganti EM, Kerr PG, Chadban SJ, Zimmet PZ, Atkins RC. Health-related quality of life in Australian adults with renal insufficiency: a population-based study. Am J Kidney Dis 2003; 41: 596–604. - PubMed
-
- Kondrashova A, Reunanen A, Romanov A, Karvonen A, Viskari H, Vesikari T et al. A six-fold gradient in the incidence of type 1 diabetes at the eastern border of Finland. Ann Med 2005; 37: 67–72. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
