Nonenzymatic copying of RNA templates containing all four letters is catalyzed by activated oligonucleotides
- PMID: 27351102
- PMCID: PMC4959843
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.17756
Nonenzymatic copying of RNA templates containing all four letters is catalyzed by activated oligonucleotides
Abstract
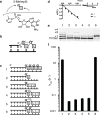
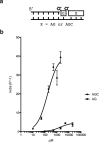
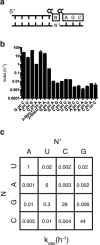
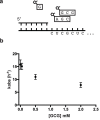
The nonenzymatic replication of RNA is a potential transitional stage between the prebiotic chemistry of nucleotide synthesis and the canonical RNA world in which RNA enzymes (ribozymes) catalyze replication of the RNA genomes of primordial cells. However, the plausibility of nonenzymatic RNA replication is undercut by the lack of a protocell-compatible chemical system capable of copying RNA templates containing all four nucleotides. We show that short 5'-activated oligonucleotides act as catalysts that accelerate primer extension, and allow for the one-pot copying of mixed sequence RNA templates. The fidelity of the primer extension products resulting from the sequential addition of activated monomers, when catalyzed by activated oligomers, is sufficient to sustain a genome long enough to encode active ribozymes. Finally, by immobilizing the primer and template on a bead and adding individual monomers in sequence, we synthesize a significant part of an active hammerhead ribozyme, forging a link between nonenzymatic polymerization and the RNA world.
Keywords: RNA; RNA polymerization; biochemistry; information copying; none; origin of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures







References
-
- Beaucage SL, Caruthers MH. Deoxynucleoside phosphoramidites—A new class of key intermediates for deoxypolynucleotide synthesis. Tetrahedron Letters. 1981;22:1859–1862. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)90461-7. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

