The Impact of Macro-and Micronutrients on Predicting Outcomes of Critically Ill Patients Requiring Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
- PMID: 27352307
- PMCID: PMC4924859
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156634
The Impact of Macro-and Micronutrients on Predicting Outcomes of Critically Ill Patients Requiring Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
Abstract
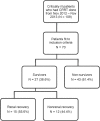
Critically ill patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) who receive renal replacement therapy (RRT) have very high mortality rate. During RRT, there are markedly loss of macro- and micronutrients which may cause malnutrition and result in impaired renal recovery and patient survival. We aimed to examine the predictive role of macro- and micronutrients on survival and renal outcomes in critically ill patients undergoing continuous RRT (CRRT). This prospective observational study enrolled critically ill patients requiring CRRT at Intensive Care Unit of King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital from November 2012 until November 2013. The serum, urine, and effluent fluid were serially collected on the first three days to calculate protein metabolism including dietary protein intake (DPI), nitrogen balance, and normalized protein catabolic rate (nPCR). Serum zinc, selenium, and copper were measured for micronutrients analysis on the first three days of CRRT. Survivor was defined as being alive on day 28 after initiation of CRRT.Dialysis status on day 28 was also determined. Of the 70 critically ill patients requiring CRRT, 27 patients (37.5%) survived on day 28. The DPI and serum albumin of survivors were significantly higher than non-survivors (0.8± 0.2 vs 0.5 ±0.3g/kg/day, p = 0.001, and 3.2±0.5 vs 2.9±0.5 g/dL, p = 0.03, respectively) while other markers were comparable. The DPI alone predicted patient survival with area under the curve (AUC) of 0.69. A combined clinical model predicted survival with AUC of 0.78. When adjusted for differences in albumin level, clinical severity score (APACHEII and SOFA score), and serum creatinine at initiation of CRRT, DPI still independently predicted survival (odds ratio 4.62, p = 0.009). The serum levels of micronutrients in both groups were comparable and unaltered following CRRT. Regarding renal outcome, patients in the dialysis independent group had higher serum albumin levels than the dialysis dependent group, p = 0.01. In conclusion, in critically ill patients requiring CRRT, DPI is a good predictor of patient survival while serum albumin is a good prognosticator of renal outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of early initiation of continuous renal replacement therapy based on the KDIGO classification on the prognosis of critically ill patients with acute kidney injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016 Mar;28(3):246-51. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016. PMID: 29917340 Chinese.
-
Predictive value of RIFLE classification on prognosis of critically ill patients with acute kidney injury treated with continuous renal replacement therapy.Chin Med J (Engl). 2009 May 5;122(9):1020-5. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009. PMID: 19493435
-
[Influence of time of initiation of continuous renal replacement therapy on prognosis of critically ill patients with acute kidney injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2013 Jul;25(7):415-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2013.07.012. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2013. PMID: 23834940 Chinese.
-
Accelerated versus standard initiation of renal replacement therapy for critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCT studies.Crit Care. 2021 Jan 5;25(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03434-z. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33402204 Free PMC article.
-
Renal replacement therapy for AKI: When? How much? When to stop?Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2017 Sep;31(3):371-385. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2017. PMID: 29248144 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors Associated with In-Hospital Mortality after Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy for Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 26;17(23):8781. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17238781. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33256008 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Supra-Hemodiafiltration in Traumatic Rhabdomyolysis and Acute Kidney Injury: A Case Report.Case Rep Nephrol Dial. 2021 Feb 3;11(1):26-35. doi: 10.1159/000507424. eCollection 2021 Jan-Apr. Case Rep Nephrol Dial. 2021. PMID: 33708797 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional management of children with acute kidney injury-clinical practice recommendations from the Pediatric Renal Nutrition Taskforce.Pediatr Nephrol. 2023 Nov;38(11):3559-3580. doi: 10.1007/s00467-023-05884-3. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Pediatr Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36939914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Factors Associated with Hypermetabolism and Hypometabolism in Critically Ill AKI Patients.Nutrients. 2018 Apr 19;10(4):505. doi: 10.3390/nu10040505. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29671764 Free PMC article.
-
Can Serum Nutritional Related Biomarkers Predict Mortality Of Critically Ill Older Patients With Acute Kidney Injury?Clin Interv Aging. 2019 Oct 18;14:1763-1769. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S218973. eCollection 2019. Clin Interv Aging. 2019. PMID: 31695346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wald R, Shariff SZ, Adhikari NK, Bagshaw SM, Burns KE, Friedrich JO, et al. The association between renal replacement therapy modality and long-term outcomes among critically ill adults with acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study*. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:868–77. 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000042 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fiaccadori E, Parenti E, Maggiore U. Nutritional support in acute kidney injury. J Nephrol. 2008;21:645–56. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical