Effect of Moderate Hepatic Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Roxadustat, an Oral Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor
- PMID: 27352308
- PMCID: PMC4987405
- DOI: 10.1007/s40261-016-0422-y
Effect of Moderate Hepatic Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Roxadustat, an Oral Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor
Abstract
Background and objective: Roxadustat is a hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor in phase III development for the treatment of anaemia associated with chronic kidney disease. This study evaluated the effects of moderate hepatic impairment on roxadustat pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and tolerability.
Methods: This was an open-label study in which eight subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (liver cirrhosis Child-Pugh score 7-9) and eight subjects with normal hepatic function (matched for body mass index, age and sex) received a single oral 100 mg roxadustat dose under fasted conditions. Blood samples were collected until 144 h post-dose in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment and until 96 h post-dose in subjects with normal hepatic function.
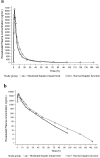
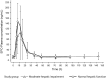
Results: In subjects with moderate hepatic impairment, area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) from the time of drug administration to infinity (AUC∞) and observed maximum concentration (C max) were 23 % higher [geometric least-squares mean ratio (GMR) 123 %; 90 % CI 86.1-175] and 16 % lower (GMR 83.6 %; 90 % CI 67.5-104), respectively, than in subjects with normal hepatic function. Mean terminal half-life (t ½) appeared to be longer (17.7 vs. 12.8 h) in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment, however intersubject variability on apparent total systemic clearance after single oral dosing (CL/F), apparent volume of distribution at equilibrium after oral administration (V z/F) and t ½ was approximately twofold higher. Erythropoietin (EPO) baseline-corrected AUC from administration to the last measurable EPO concentration (AUCE,last) and maximum effect (E max) were 31 % (GMR 68.95 %; 90 % CI 29.29-162.29) and 48 % (GMR 52.29 %; 90 % CI 28.95-94.46) lower, respectively, than in subjects with normal hepatic function. The single oral roxadustat dose was generally well tolerated.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated the effect of moderate hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of roxadustat relative to subjects with normal hepatic function. These differences are not expected to be of clinical significance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roxadustat: First Global Approval.Drugs. 2019 Apr;79(5):563-572. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01077-1. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30805897 Review.
-
Effect of Kidney Function and Dialysis on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Roxadustat, an Oral Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2021 Jan;46(1):141-153. doi: 10.1007/s13318-020-00658-w. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2021. PMID: 33165773 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oral Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor Roxadustat (FG-4592) for Treatment of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Placebo-Controlled Study of Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Profiles in Hemodialysis Patients.J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Nov;60(11):1432-1440. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1648. Epub 2020 Jun 30. J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32603526 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Moderate Hepatic Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics of Vadadustat, an Oral Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2021 Aug;10(8):950-958. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.927. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2021. PMID: 33661566 Clinical Trial.
-
The prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor roxadustat: Paradigm in drug discovery and prospects for clinical application beyond anemia.Drug Discov Today. 2020 Jul;25(7):1262-1269. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.04.017. Epub 2020 May 4. Drug Discov Today. 2020. PMID: 32380083
Cited by
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Roxadustat.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022 Mar;61(3):347-362. doi: 10.1007/s40262-021-01095-x. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022. PMID: 34905154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roxadustat: First Global Approval.Drugs. 2019 Apr;79(5):563-572. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01077-1. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30805897 Review.
-
Liver Zonation in Health and Disease: Hypoxia and Hypoxia-Inducible Transcription Factors as Concert Masters.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 11;20(9):2347. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092347. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31083568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Activators in Renal Anemia: Current Clinical Experience.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019 Jul;26(4):253-266. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2019.04.004. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019. PMID: 31477256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of hypoxia-inducible factor stabilizers in the treatment of anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Sep 18;12:3003-3011. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S175887. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30271115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- KDIGO. Clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013;3:1–150. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

