Antibacterial Efficacy of Eravacycline In Vivo against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Organisms
- PMID: 27353265
- PMCID: PMC4958151
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00366-16
Antibacterial Efficacy of Eravacycline In Vivo against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Organisms
Abstract
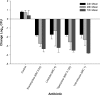
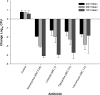
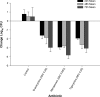
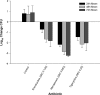
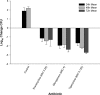
Members of the tetracycline class are frequently classified as bacteriostatic. However, recent findings have demonstrated an improved antibacterial killing profile, often achieving ≥3 log10 bacterial count reduction, when such antibiotics have been given for periods longer than 24 h. We aimed to study this effect with eravacycline, a novel fluorocycline, given in an immunocompetent murine thigh infection model over 72 h against two methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates (eravacycline MICs = 0.03 and 0.25 μg/ml) and three Enterobacteriaceae isolates (eravacycline MICs = 0.125 to 0.25 μg/ml). A humanized eravacycline regimen, 2.5 mg/kg of body weight given intravenously (i.v.) every 12 h (q12h), demonstrated progressively enhanced activity over the 72-h study period. A cumulative dose response in which bacterial density was reduced by more than 3 log10 CFU at 72 h was noted over the study period in the two Gram-positive isolates, and eravacycline performed similarly to comparator antibiotics (tigecycline, linezolid, and vancomycin). A cumulative dose response with eravacycline and comparators (tigecycline and meropenem) over the study period was also observed in the Gram-negative isolates, although more variability in bacterial killing was observed for all antibacterial agents. Overall, a bacterial count reduction of ≥3 log was achieved in one of the three isolates with both eravacycline and tigecycline, while meropenem achieved a similar endpoint against two of the three isolates. Bactericidal activity is typically defined in vitro over 24 h; however, extended regimen studies in vivo may demonstrate an improved correlation with clinical outcomes by better identification of antimicrobial effects.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2013. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2013. US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, Atlanta, GA. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

