Zonulin Regulates Intestinal Permeability and Facilitates Enteric Bacteria Permeation in Coronary Artery Disease
- PMID: 27353603
- PMCID: PMC4926221
- DOI: 10.1038/srep29142
Zonulin Regulates Intestinal Permeability and Facilitates Enteric Bacteria Permeation in Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
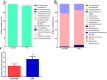
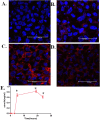
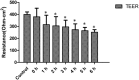
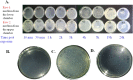
Several studies have reported an association between enteric bacteria and atherosclerosis. Bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene belong to Enterobacteriaceae have been detected in atherosclerotic plaques. How intestinal bacteria go into blood is not known. Zonulin reversibly modulate intestinal permeability (IP), the circulating zonulin levels were increased in diabetes, obesity, all of which are risk factors for atherosclerosis. It is unclear whether the circulating zonulin levels were changed in coronary artery disease (CAD) patients and modulate IP. The 16S rRNA gene of bacteria in blood sample was checked by 454 pyrosequencing. The zonulin levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) methods. The distribution of zonulin was detected by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. Bacteria and Caco-2 cell surface micro-structure were checked by transmission electron microscopy. A high diversity of bacterial 16S rRNA gene can be detected in samples from CAD patients, most of them (99.4%) belong to Enterobacteriaceaes, eg. Rahnella. The plasma zonulin levels were significantly higher in CAD patients. Pseudomonas fluorescens exposure significantly increased zonulin expression and decreased IP in a time dependent manner. The elevated zonulin increase IP and may facilitate enteric translocation by disassembling the tight junctions, which might explain the observed high diversity of bacterial 16S rRNA genes in blood samples.
Figures
References
-
- Mozaffarian D. et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics–2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 131, e29–322 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Hansson G. K. Inflammation, Atherosclerosis, and Coronary Artery Disease. N Engl J Med. 352, 1685–95 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Kalayoglu M. V1., Libby P. & Byrne G. I. Chlamydia pneumoniae as an emerging risk factor in cardiovascular disease. JAMA. 288, 2724–31 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

