Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling impacts lymphocyte migration, inflammation and infection
- PMID: 27354294
- PMCID: PMC5985508
- DOI: 10.1093/femspd/ftw063
Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling impacts lymphocyte migration, inflammation and infection
Abstract
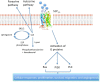
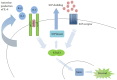
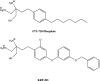
Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) is a sphingosine containing lipid intermediate obtained from ceramide. S1P is known to be an important signaling molecule and plays multiple roles in the context of immunity. This lysophospholipid binds and activates G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) known as S1P receptors 1-5 (S1P1-5). Once activated, these GPCRs mediate signaling that can lead to alterations in cell proliferation, survival or migration, and can also have other effects such as promoting angiogenesis. In this review, we will present evidence demonstrating a role for S1P in lymphocyte migration, inflammation and infection, as well as in cancer. The therapeutic potential of targeting S1P receptors, kinases and lyase will also be discussed.
Keywords: FTY720; S1P; lymphocyte trafficking; sphingosine.
© FEMS 2016. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate in hematologic malignancies.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Nov;11(9):794-8. doi: 10.2174/187152011797655122. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21707492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To fingolimod and beyond: The rich pipeline of drug candidates that target S1P signaling.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Nov;113(Pt A):521-532. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.09.025. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27663260 Review.
-
Finding a Way Out: S1P Signaling and Immune Cell Migration.Annu Rev Immunol. 2020 Apr 26;38:759-784. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-081519-083952. Annu Rev Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32340572 Review.
-
Sphingosine kinase signalling in immune cells: potential as novel therapeutic targets.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jan;1784(1):66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.07.013. Epub 2007 Aug 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 17913601 Review.
-
[Effects of sphingosine 1-phosphate on functions of T cell - review].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2005 Aug;13(4):718-22. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 16129068 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Lipid metabolism in B cell biology.Mol Oncol. 2024 Jul;18(7):1795-1813. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13560. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Mol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38013654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor Blockade Affects Pro-Inflammatory Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages and Relieves Mouse Fatty Liver Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 22;20(19):4695. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194695. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31546702 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate and Ceramide-1-Phosphate in Inflammation and Cancer.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:4806541. doi: 10.1155/2017/4806541. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29269995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asymptomatic COVID-19: disease tolerance with efficient anti-viral immunity against SARS-CoV-2.EMBO Mol Med. 2021 Jun 7;13(6):e14045. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202114045. Epub 2021 May 27. EMBO Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33961735 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles for Sphingolipids in Cardiometabolic Disease: A Rational Therapeutic Target?Nutrients. 2024 Sep 28;16(19):3296. doi: 10.3390/nu16193296. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39408263 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anelli V, Gault CR, Cheng AB, et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 is up-regulated during hypoxia in U87MG glioma cells. Role of hypoxia-inducible factors 1 and 2. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:3365–75. - PubMed
-
- Arish M, Husein A, Kashif M, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling: unraveling its role as a drug target against infectious diseases. Drug Discov Today. 2016;21:133–42. - PubMed
-
- Bolli MH, Abele S, Birker M, et al. Novel S1P(1) receptor agonists–part 3: from thiophenes to pyridines. J Med Chem. 2014;57:110–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

