Association Between Plasma Genotyping and Outcomes of Treatment With Osimertinib (AZD9291) in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 27354477
- PMCID: PMC5035123
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2016.66.7162
Association Between Plasma Genotyping and Outcomes of Treatment With Osimertinib (AZD9291) in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have demonstrated potent activity against TKI resistance mediated by EGFR T790M. We studied whether noninvasive genotyping of cell-free plasma DNA (cfDNA) is a useful biomarker for prediction of outcome from a third-generation EGFR-TKI, osimertinib.
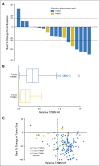
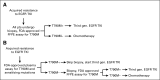
Methods: Plasma was collected from all patients in the first-in-man study of osimertinib. Patients who were included had acquired EGFR-TKI resistance and evidence of a common EGFR-sensitizing mutation. Genotyping of cell-free plasma DNA was performed by using BEAMing. Plasma genotyping accuracy was assessed by using tumor genotyping from a central laboratory as reference. Objective response rate (ORR) and progression-free survival (PFS) were analyzed in all T790M-positive or T790M-negative patients.
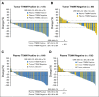
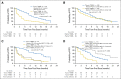
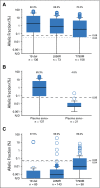
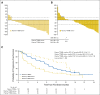
Results: Sensitivity of plasma genotyping for detection of T790M was 70%. Of 58 patients with T790M-negative tumors, T790M was detected in plasma of 18 (31%). ORR and median PFS were similar in patients with T790M-positive plasma (ORR, 63%; PFS, 9.7 months) or T790M-positive tumor (ORR, 62%; PFS, 9.7 months) results. Although patients with T790M-negative plasma had overall favorable outcomes (ORR, 46%; median PFS, 8.2 months), tumor genotyping distinguished a subset of patients positive for T790M who had better outcomes (ORR, 69%; PFS, 16.5 months) as well as a subset of patients negative for T790M with poor outcomes (ORR, 25%; PFS, 2.8 months).
Conclusion: In this retrospective analysis, patients positive for T790M in plasma have outcomes with osimertinib that are equivalent to patients positive by a tissue-based assay. This study suggests that, upon availability of validated plasma T790M assays, some patients could avoid a tumor biopsy for T790M genotyping. As a result of the 30% false-negative rate of plasma genotyping, those with T790M-negative plasma results still need a tumor biopsy to determine presence or absence of T790M.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01802632.
© 2016 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Figures


Comment in
-
Implications of Blood-Based T790M Genotyping and Beyond in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2016 Oct 1;34(28):3361-2. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.68.3458. Epub 2016 Jul 18. J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27432918 No abstract available.
-
Harnessing plasma genotyping for precision therapy against lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2016 Oct;8(10):E1387-E1390. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.10.95. J Thorac Dis. 2016. PMID: 27867637 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Are we ready to introduce T790M plasma analysis in the follow up of patients with NSCLC under treatment with EGFR-TKI?Ann Transl Med. 2016 Dec;4(24):504. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.11.70. Ann Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 28149866 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:947–957. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non–small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3327–3334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

